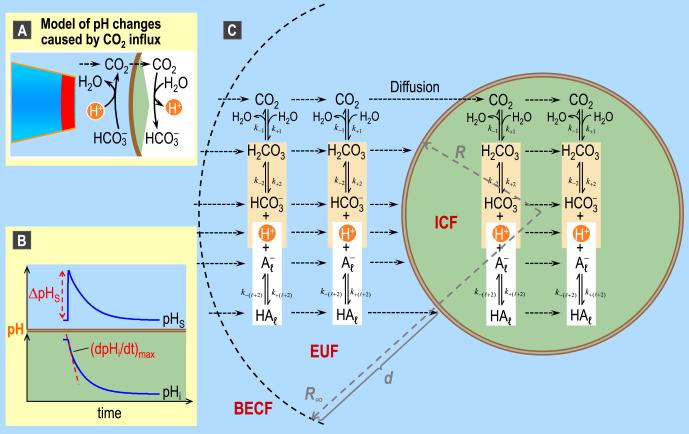
Fig. 8.
pH changes caused by CO2 influx and major features of the mathematical model of Somersalo et al. (2012). A: Model of acid-base chemistry at the outer surface and inner surface of the plasma membrane as CO2 enters into the cell. B: Representative intracellular (pHi) and surface pH (pHS) transients caused by CO2 influx. These pHi and pHS trajectories are the result of a simulation, and are the same trajectories shown as the blue records in Fig. 11. C: Major components of the mathematical model for a spherical cell with radial symmetry. BECF, bulk extracellular fluid; EUF, extracellular unconvected fluid; ICF, intracellular fluid; k, a rate constant. Panel C is modified from Fig. 2 in Somersalo et al. (2012).