Figure 2.
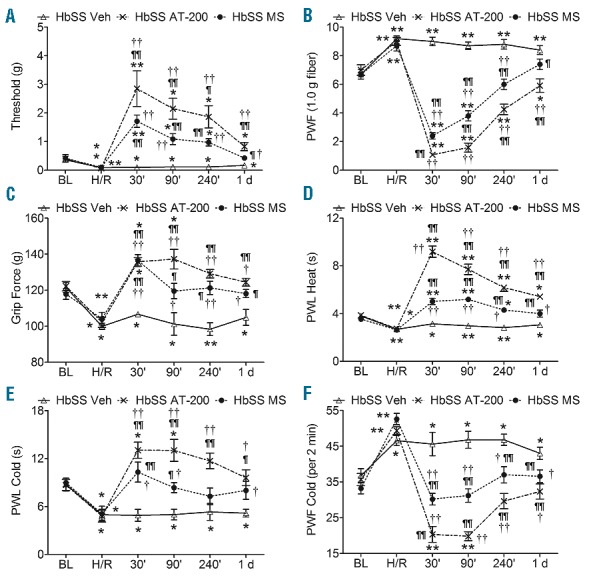
AT-200 attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation evoked pain. Sickle mice were exposed to 3 h of hypoxia and 1 h of reoxygenation at room air and treated with vehicle, AT-200, or morphine. Sensory testing was performed at baseline, immediately following H/R and after drug treatments at indicated times. (A and B) mechanical threshold, and supra-threshold; (C) deep tissue hyperalgesia, and (D–F) thermal sensitivity to heat and cold. Open triangles with solid lines, crosses with dashed lines, and solid circles with dashed lines represent vehicle, AT-200, and morphine treatment, respectively. Statistical significance was calculated by comparing each value with BL (*) or with H/R (¶); and between vehicle and AT-200 (†). *P<0.05 and **P<0.005 compared to BL; ¶P< 0.05 and ¶¶P<0.005 compared to H/R; and †P<0.05 and ††P<0.005 compared to vehicle for that timepoint. Mean age of mice ± SEM in months were, HbSS-BERK Vehicle (n=10), 20.9±1.7, and HbSS-BERK AT-200 (n=12), 21.2±1.7, and HbSS-BERK MS (n=10), 21.4±1.6. BL, baseline; H/R: hypoxia/reoxygenation; Veh: vehicle; MS: morphine sulfate; PWF: paw withdrawal frequency; PWL: paw withdrawal latency.
