Figure 2.
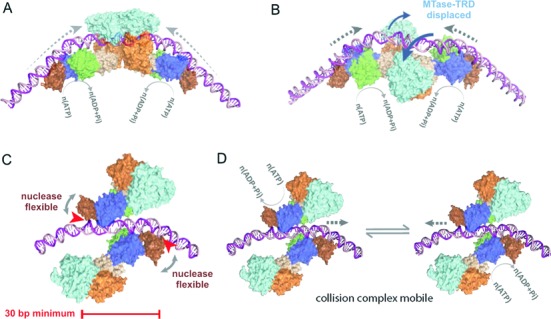
Structural models for collision and cleavage of DNA by Type ISP restriction enzymes. Structures based on PDB 4XQK (8). (A) Head-on collision between two translocating enzymes with the MTase-TRD domains engaged with the DNA results in placement of the nuclease domains ∼75 bp apart. (B and C) To accommodate the closer placement of the nuclease domains, the MTase-TRD domains swing off the DNA and the helicase domains collide, placing the nuclease domains at the measured ∼30 bp minimum (8). (D) To produce DNA nicks that are sufficiently closely-spaced to form a dsDNA break, ATP hydrolysis drives a back-and-forth mobility of the collision complex (see Figure 1A).
