Figure 1.
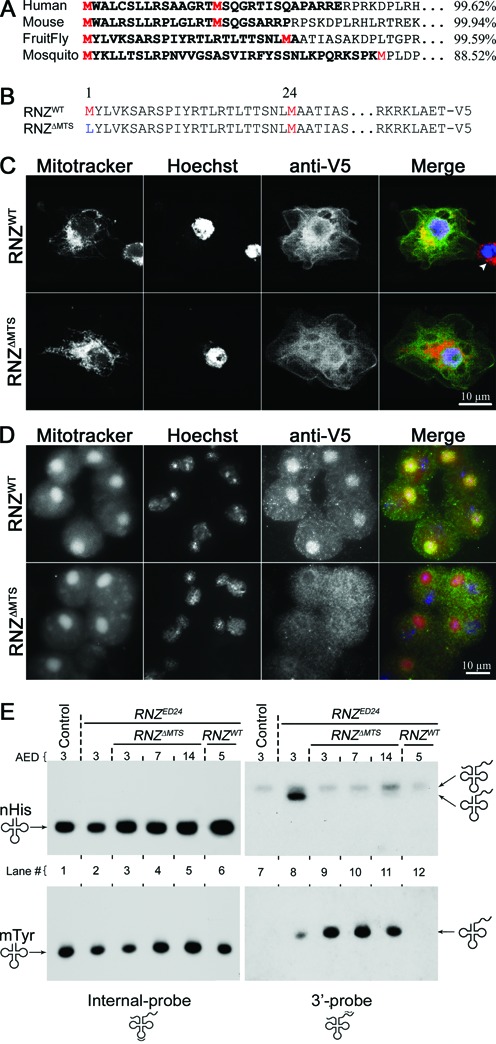
Mitochondria-specific knockout of dRNaseZ. (A) N-terminal sequences of RNase ZL from different species. The mitochondria import probabilities (right) were calculated using MitoProt. Two initiating methionines are in red. The putative MTS is in bold. (B) The N-termini and C-termini of proteins encoded by RNZWT and RNZΔMTS constructs. Methionines are in red and the mutated amino acid is in blue. V5-tags are attached to the C-termini of WT and mutant proteins. (C,D) Immunostaining of S2 cultured cells (C) and testes (D) expressing RNZWT and RNZΔMTS proteins. In merge: mitochondria (Mitotracker) are red, DNA (Hoechst) is blue, and anti-V5 is green. (C) S2 cells transfected with plasmids encoding RNZWT or RNZΔMTS proteins. Arrowhead indicates a non-transfected cell. (D) Onion stage spermatids from transgenic males carrying the genRNZWT or genRNZΔMTS construct. Note that in (C,D) RNZWT co-localizes with mitochondria (yellow), while RNZΔMTS does not. (E) Northern blot analysis of RNA samples from WT control (lane 1 and 7), RNZED24 KO (lane 2 and 8) and RNZΔMTS (lane 3–5 and 9–11), or RNZWT (lane 6 and 12) rescued KO larvae. The internal-probe detects mature nuclear Histidine (nHis) and mitochondrial Tyrosine (mtTyr) tRNAs; the 3′-probe detects primary transcripts and processing intermediates.
