Figure 7.
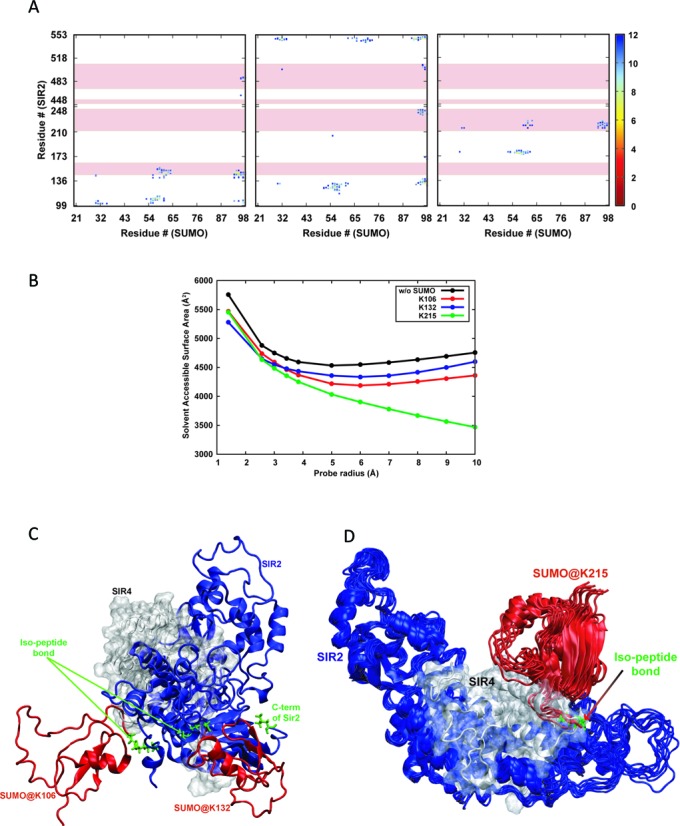
Molecular modeling of Sir2–Sir4 interaction. (A) Contact maps corresponding to Sir2–Sir4 interactions where the Sir2 protein is sumoylated at K106, K132 and K216. Those distances above 12 Å are not plotted for clarity. The pink highlights correspond to the residues on Sir2 that interact with Sir4. (B) Average solvent accessible surface areas of the Sir2 residues that take part in Sir4 binding in unsumoylated and sumoylated Sir2 with respect to the probe radius (see text). (C) Representation of the structures of sumoylated Sir2 at K106 and K132, and (D) a small ensemble of structures of sumoylated Sir2 at K215 and the experimental structure of Sir2–Sir4 binary complex aligned based on the Sir2 protein. Sir2, Sir4 and SUMO are depicted in blue, gray and red colors, respectively, and the isopeptide bonds along with the two residues are in green stick representation.
