Figure 1.
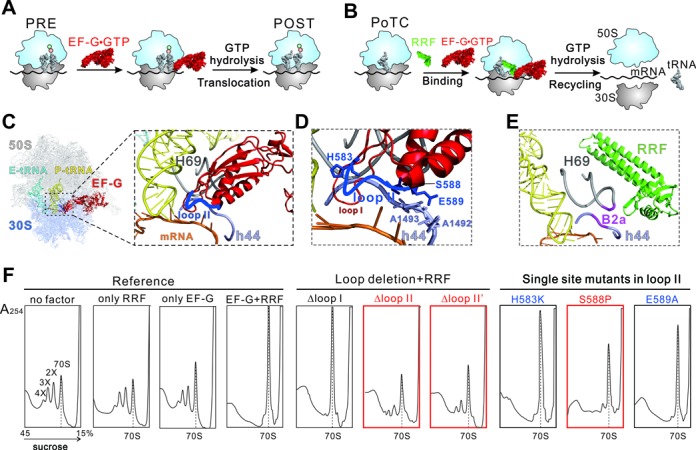
Function of EF-G during translocation and ribosome recycling. (A) Brief model of EF-G catalyzed translocation. The process from PRE to POST state is promoted by GTP hydrolysis. (B) Brief model of ribosome recycling process. EF-G and RRF function together to dissociate the PoTC into subunits. (C-E) Interactions of EF-G loop II (blue) and RRF (green) with ribosomal intersubunit bridge B2a. The B2a contains H69 (gray) of 23S rRNA and h44 (lavender) of 16S rRNA. Both EF-G and RRF interact with this bridge. The model of the POST-state ribosome(C, D) was extracted from a previous crystal structure (PDB 4V5F (19)). The model of PoTC•RRF (E) was also from a crystallography study (PDB 4V9D(26)). (F) Effect of loop II deletion and single site mutants on ribosome breakdown. The ribosome sedimentation pattern was analyzed by 15–45% sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. Fractions were collected from the bottom to the top of the tube and measured at A254. The peaks corresponding to the 70S ribosome, disome, trisome and tetrasome are marked as 70S, 2X, 3X and 4X, respectively. The 70S position is indicated with dashed line throughout. The red colored mutants are effective in both recycling and tRNA translocation, while the blue ones only in tRNA translocation.
