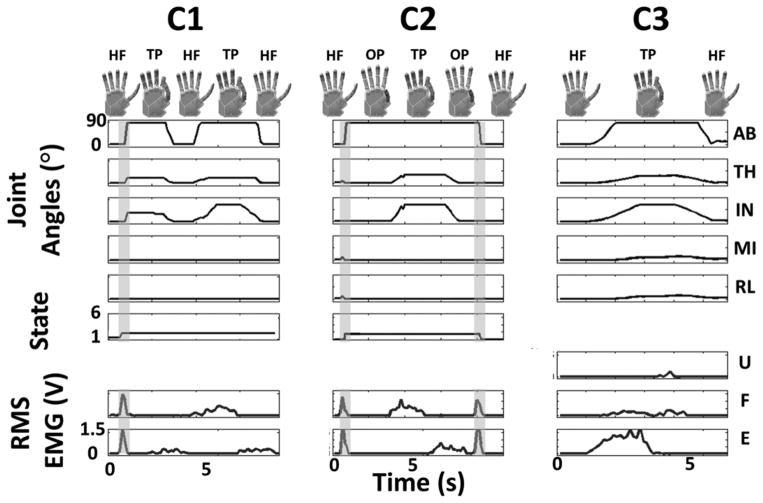
Figure 5.
Transformation of root-mean-square (RMS) electromyography (EMG) signals into five joint angles. Smoothed EMG signal in red from extensor digitorum (E), flexor digitorum (F), and extensor carpi ulnaris (U) showed muscle activity after filtering and tuning. Joint angle traces from top to bottom for thumb abduction (AB), thumb flexion (TH), index flexion (IN), middle flexion (MI), and ring/little flexion (RL) corresponded with hand posture shown, including hand flat (HF), tip prehension (TP), and opposition (OP). State and posture of controller 1 (C1) and controller 2 (C2) is depicted, and cocontraction trigger signal is highlighted by vertical gray bar. Note that controller 3 (C3) does not require trigger signal since postural control architecture controls hand posture in continuous domain without discrete states.