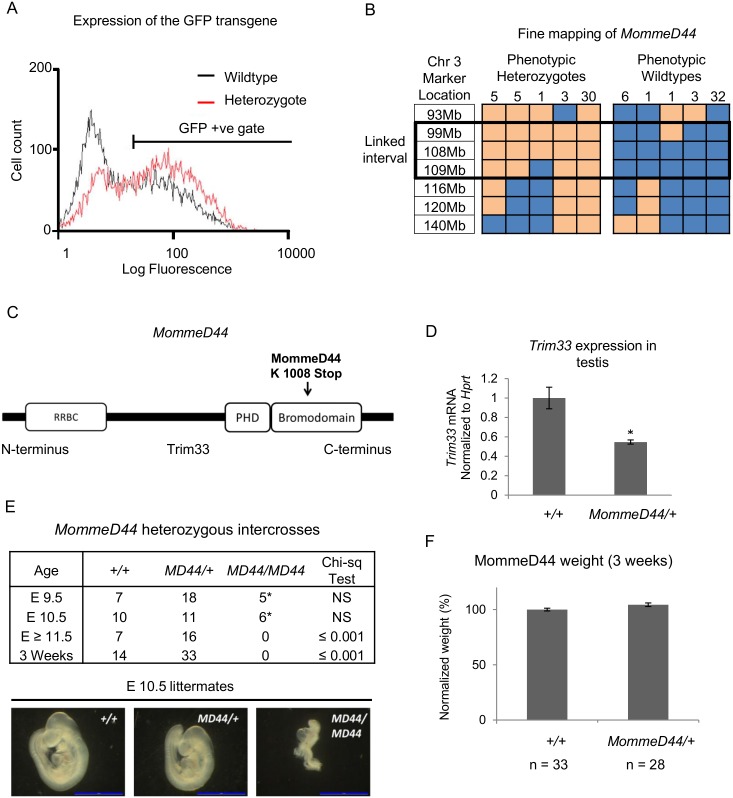
Fig 1. The Momme44 mutation produces a null allele of Trim33.
(A) Representative GFP profiles for MommeD44 wildtype (black) and heterozygous (red) mice are shown by the numbers of erythrocytes expressing GFP along a log scale of fluorescence. A GFP gate shows cells positive for GFP expression. (B) Genetic mapping of phenotypically heterozygous and wildtype F2 (C57/FVB) mice indicates the boundaries for the MommeD44 mutation. FVB/C57 genotype SNPs are shaded yellow and C57/C57 genotype SNPs are shaded blue. Numbers of mice representing each SNP profile are indicated. (C) The MommeD44 mutation is located in the Bromodomain of Trim33 and changes a leucine to a stop codon. (D) Mice heterozygous for the MommeD44 mutation had significantly reduced levels of Trim33 mRNA, normalized to the housekeeping gene Hprt, in the testis. * p value ≤ 0.05, error bars indicate SEM, n ≥ 3 mice per genotype. (E) Embryos from heterozygous intercrosses show that MommeD44 homozygous embryos die during early development. Astericies indicate abnormal embryos, represented by E10.5 MD44/MD44 image. (F) The weight of MommeD44 heterozygous mice (MD44/+) at weaning. The weight of each mouse was normalized to the average weight of wildtype mice from each litter, error bars indicate SEM,* p value ≤ 0.05.