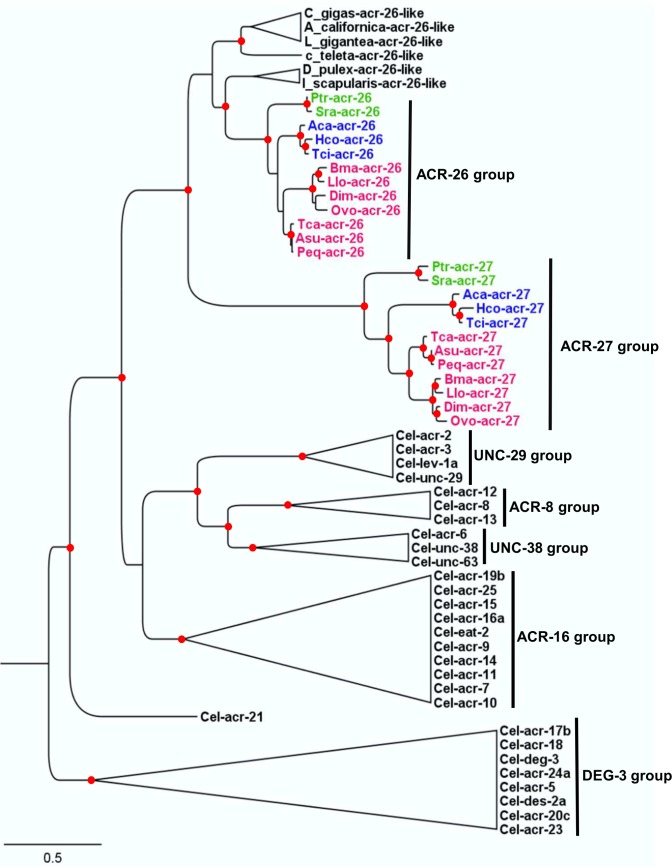
Fig 1. Maximum likelihood tree showing relationships of ACR-26 and ACR-27 acetylcholine receptor (AChR) subunits from parasitic nematodes with C. elegans AChR subunits.
Tree was built upon an alignment of AChR subunit sequences excluding the predicted signal peptide and the highly variable region between TM3 and TM4. Potential homologs of ACR-26 identified in the molluscs, Aplysia californica, Crassostrea gigas, Lottia gigantean, the annelid Capitella telata and the arthropods Ixodes scapularis and Daphnia pulex were also included in the analysis. The tree was rooted with DEG-3 group subunit sequences. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of substitutions per amino acid. Scale bar represents the number of substitution per site. Red dots at the nodes indicate bootstrap values >70%. Accession numbers for sequences used in the phylogenetic analysis are provided in Materials and Methods section. C. elegans AChR subunit groups were named as proposed by Mongan et al. [35]. The three letter prefixes in AChR subunit gene names, Cel, Tci, Hco, Aca, Tca, Peq, Ovo, Dim, Llo, Bma, Sra and Ptr refer to Caenorhabditis elegans, Teladorsagia circumcincta, Haemonchus contortus, Ancylostoma caninum, Toxocara canis, Parascaris equorum, Onchocerca volvulus, Dirofilaria immitis, Loa loa, Brugia malayi, Strongyloides ratti and Parastrogyloides trichosuri respectively. Parasitic nematode species belonging to Clade III, VI and V are highlighted in red, green and blue respectively.