Figure 2. The lone variant in the 99% credible set at the MTNR1B locus affects FOXA2-bound enhancer activity.
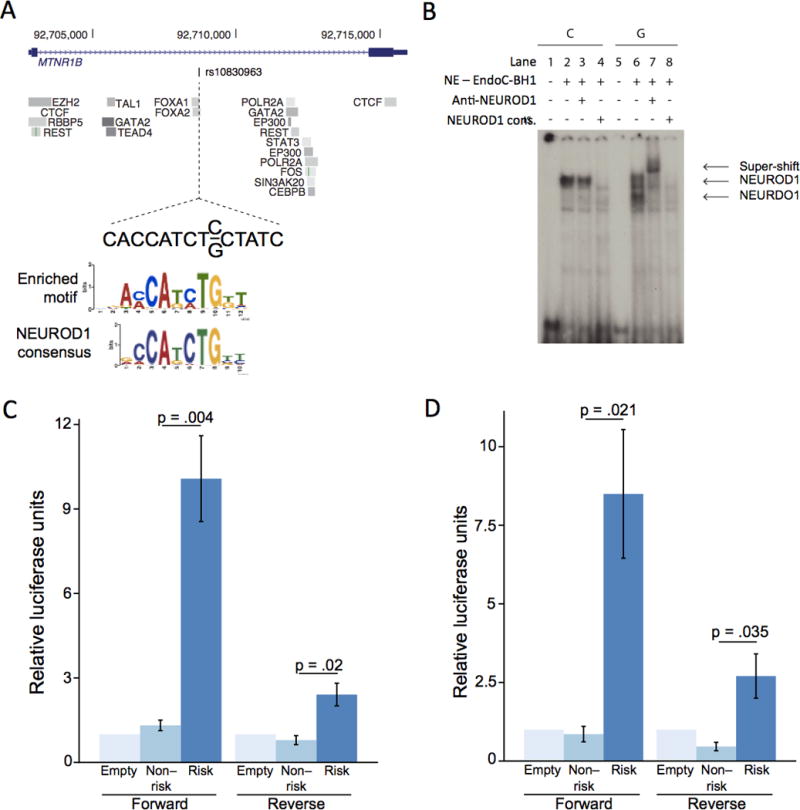
(A) The intronic variant, rs10830963, has 99.8% probability of driving the association signal at the MTRN1B locus. This variant overlaps a FOXA2 binding site, and the risk allele G is predicted to create a de novo recognition motif, which closely matches the NEUROD1 consensus. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of a 25bp fragment surrounding both alleles in EndoC-βH1 cell extracts. Proteins were bound to both alleles. In the presence of a NEUROD1 antibody, only the risk allele band was super-shifted, and in the presence of an unlabelled NEUROD1 consensus probe, the signal was competed away. NE: nuclear extract. (C, D) The 224bp sequence surrounding each allele was cloned into a luciferase reporter construct containing a minimal promoter and tested for luciferase activity in (C) EndoC-βH1 and (D) HepG2 cells (n=3 for each cell type). Results are presented as mean ± standard error. The risk allele had significantly increased enhancer activity over the protective allele in both forward and reverse orientations in both cell types.
