Figure 7.
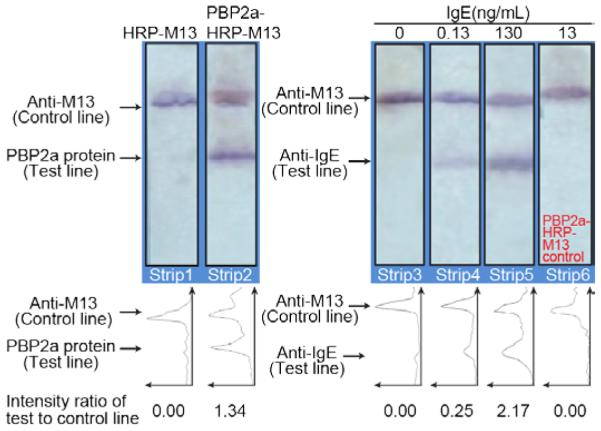
PBP2a aptamer-phage as a specificity control for IgE-aptamer-phage reporters. Strips 1 & 2; Strips with PBP2a protein and anti-M13 antibodies on the test and control lines, respectively, were made to evaluate the binding of PBP2a-M13 to PBP2a protein. A clear signal on the test line of strip 2 indicates binding of the PBP2a-phage to the PBP2a protein. Strip 1 with HRP-phage devoid of any signal, confirms that phage do not bind non-specifically to the PBP2a protein. Strips 3, 4 & 5 show the various concentrations of IgE protein (100 μL in LFA buffer) that were used. IgE binds on the anti-IgE test line. Signals on the control lines indicate the proper functioning of the assay. Strip 6; A PBP2a-M13 phage construct was passed through a strip with anti-IgE and anti-M13 lines. The anti-PBP2a aptamer on the phage did not bind to the IgE protein on the test line as indicated by the absence of any signal on the test line. Line intensity profiles as plotted by ImageJ density analyses of the LFA strips are shown below each figure. The area under each peak was numerically integrated using the ImageJ Gel Analysis Toolbox, and the average intensity of the test line divided by the intensity of the control line for each strip is also shown below each line intensity profile.
