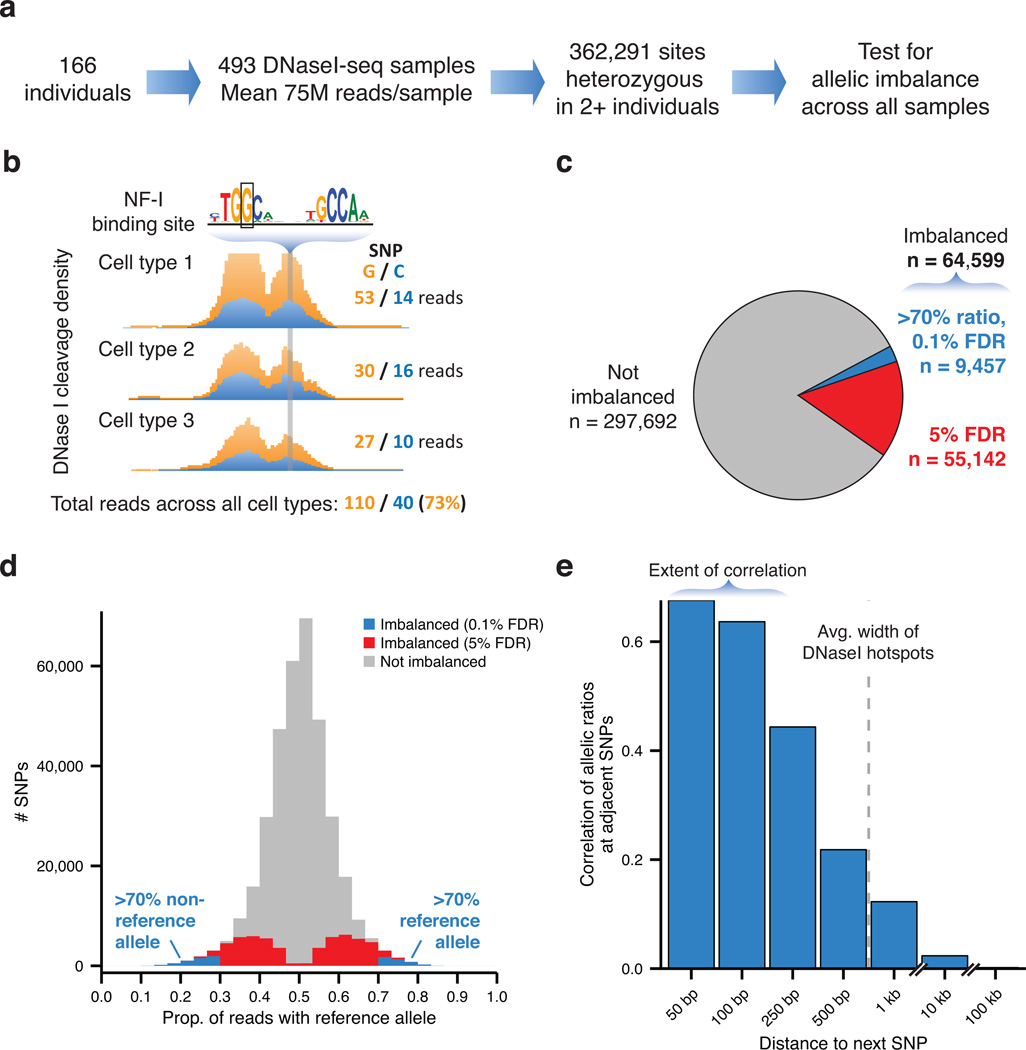
Figure 1. Identification of regulatory variants impacting DNA accessibility.
(a) Outline of experimental procedure and data set. (b) Allelic analysis of DNA accessibility at heterozygous sites. Imbalance manifests as a deviation from 50:50 in the ratio of reads mapping to two homologous chromosomes, potentially due to alteration of TF binding by the sequence variant itself. (c) Extent of imbalanced variants discovered. A strict set of imbalanced variants were identified at 0.1% FDR and >70% imbalance (blue). (d) Allelic ratios of sequencing reads relative to reference allele. A ratio of 70% represents a 2.3-fold difference in accessibility between the two alleles. (e) Pearson correlation of allelic ratios at adjacent SNPs broken down by distance to next SNP. Dashed line represents the median width of DHS hotspots overlapping SNPs in this study. Shown are SNPs in high linkage disequilibrium (r2 > 0.8) in our samples (see Supplementary Fig. 5).