Figure 2. Vocal imitation in songbirds.
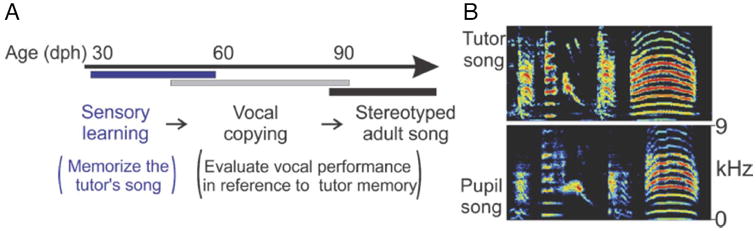
Left panel (a): Developmental timeline for zebra finch song learning. Zebra finches are a commonly studied species of songbird that learn a single song during a developmental critical period that extends from 30 to 90 days post-hatching. This critical period is composed of three phases. During the first phase young birds memorize the song of an adult model. During the second phase young birds use auditory feedback to evaluate their song imitation and slowly learn to produce a nearly perfect copy of the memorized song. During this period young birds may practice their song as much as 3,000 times a day. After 90 days of age birds begin to crystallize this adult song, leading to a highly stereotyped adult song pattern. Right panel (b): These panels show sonograms (frequency versus time plots) of an adult bird's song and imitation of the song by another bird. The song contains 4 syllables, indicated by the four separate acoustic elements and is 600 milliseconds long. Comparison of the timing and acoustic features of the songs shows clear patterns of vocal imitation. Figure modified from Roberts et al., 2012 (Fig 1a and Fig 2e) (118).
