Figure 6.
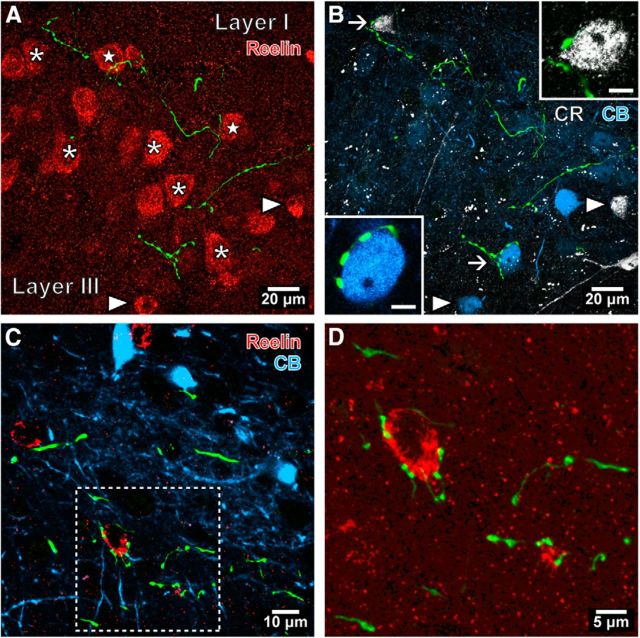
Interneuron targeting septal PV-expressing GABAergic axons in the mEC. A, B, Confocal microscopic image stacks of the same area showing labeled septal axons (green) in relation to distinct neurons visualized with different fluorophores in LII of the mEC (horizontal section; case GU41s20bb). The boutons are not associated with large reelin-immunopositive somata (red; e.g., asterisks), many of which are stellate cells that do not contain detectable levels of CR (B, white) or CB (blue). In this collapsed view of Z-stack, some septal boutons appear next to putative stellate cell somata (stars), but were not in contact in single optical slice images. Two smaller reelin-immunopositive interneurons are identified by colocalization of CR or CB (arrowheads). A CR-immunoreactive (upper arrow) interneuron and a CB-immunoreactive (lower arrow) interneuron are innervated and are shown enlarged in the insets (single optical slices, 0.38 μm thick). C, In layer V of the mEC (case GU41s20i), three reelin-immunopositive interneurons (red) are immunonegative for CB (blue). D, Septal innervation of the reelin-immunopositive interneuron soma shown in the framed area of C. Median filter was applied [(in A and B: x, y, z (radius, 1 pixel); in C and D: x, y (radius, 1 pixel)]. Maximum intensity projections of confocal image stacks: A and B, 8.82 μm; C and D, 2.36 μm.