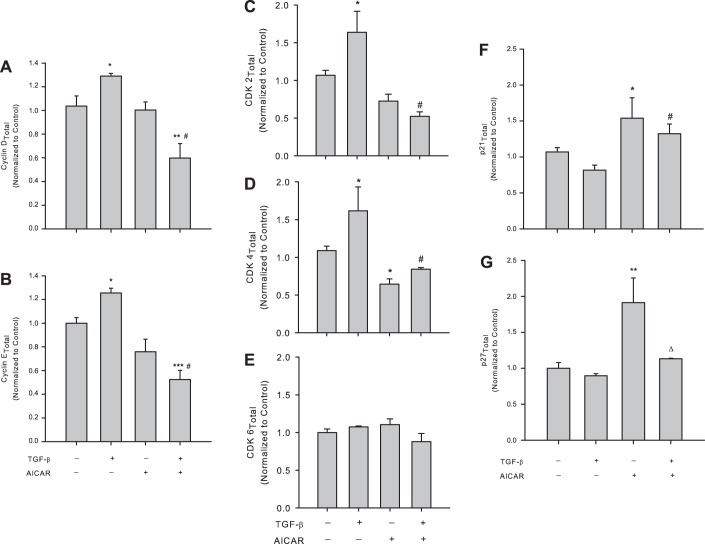
Fig. 4.
AICAR controls TGF-β1-induced cell cycle regulatory proteins. Rat A7R5 VSMCs were treated with vehicle or rTGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) with/without AICAR (1 mM) for 24 h following overnight quiescence, and cell cycle regulatory proteins cyclin D1 and cyclin E, the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 2, CDK4, and CDK6, and the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDK-I) p21 and p27 were analyzed by immunofluorescence with flow cytometry. Treatment with rTGF-β1 alone significantly increased expression of cyclin D1 (A) and cyclin E (B), and these were reversed in the presence of AICAR. AICAR alone did not significantly alter expression of cyclins D1 or E compared with vehicle controls. Treatment with rTGF-β1 alone induced expression of the cyclin E/cyclin A agonist CDK2 (C) and the cyclin D agonist CDK4 (D) compared with vehicle controls, and both were significantly reversed in the presence of AICAR. AICAR alone modestly (nonsignificantly) reduced CDK2 and significantly reduced CDK4 expression compared with controls, yet no changes were observed in CDK6 expression with any TGF-β1/AICAR regimen (E). Treatment with TGF-β1 alone failed to significantly alter p21 (F) or p27 (G) expression compared with vehicle controls, yet sole AICAR treatment induced significant elevations in both p21 and p27 compared with controls. Concomitant TGF-β1 and AICAR reversed p27 induction observed with TGF-β1 treatment alone but did not markedly alter TGF-β1-induced p21 induction. Data are presented as protein of interest normalized to total protein, with n = 3–5/treatment group. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, and ***P < 0.001 compared with vehicle controls, #P < 0.05 compared with the TGF-β1 treatment group, and ΔP < 0.05 compared with AICAR treatment alone.