Fig. 2.
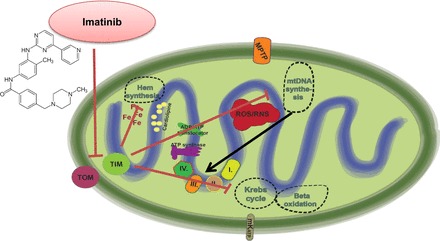
Mechanisms of imatinib cardiotoxicity. The small molecule inhibitor of the Bcr/Abl (fusion kinase of the break point cluster region of chromosome 22 and the Abelson1 gene of chromosome 9) kinase imatinib induces mitochondrial dysfunction by interfering with mitochondrial protein import machinery. Increased PRKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) activation in the endoplasmic reticulum leads to the phosphorylation eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) and to translational attenuation of translocase of the inner membrane (TIM) 23-kDa form that is essential for protein import into the mitochondrial matrix. Impaired protein import will negatively affect major mitochondrial metabolic pathways, including mitochondrial DNA synthesis, the Krebs cycle, β-oxidation, and hem synthesis. TOM, translocase of the outer membrane.
