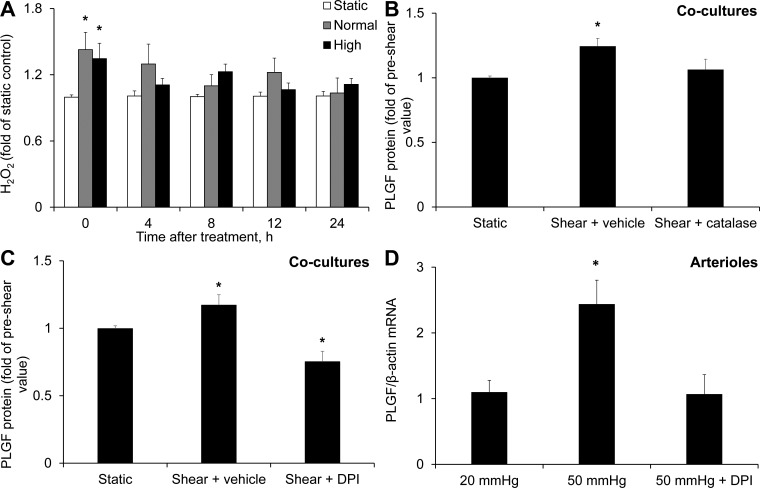
Fig. 7.
Role of H2O2 in the FSS-induced increase in PLGF protein. A: high and normal FSS significantly increased H2O2 in cocultures immediately after shear exposure compared with static control (n = 5). *P < 0.05. B: catalase (500 U/ml) blocked the effect of FSS to upregulate PLGF (n = 5). *P < 0.01. C: diphenyleneiodonium (DPI, 5 μM) also prevented the increase in PLGF protein in response to FSS and further decreased PLGF protein below static control levels (n = 5). *P < 0.01. D: DPI (5 μM) also inhibited the flow-induced increase in PLGF mRNA in cannulated arterioles [20 mmHg (n = 6), 50 mmHg (n = 5), and DPI + 50 mmHg (n = 4)]. *P < 0.01.