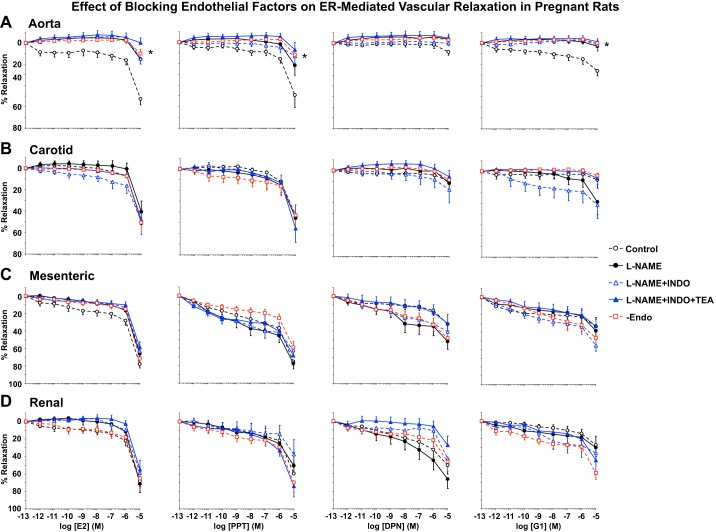
Fig. 7.
Effect of blockade of nitric oxide, prostglandins, and EDHF or endothelium removal (Endo) on the vascular relaxation effects of E2, PPT, DPN, and G1 in the aorta (A), carotid artery (B), mesenteric artery (C), and renal artery (D) of pregnant rats. Vascular segments from pregnant rats were either nontreated or pretreated with the nitric oxide inhibitor Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME; 3 × 10−4 M), cyclooxygenase inhibitor indomethacin (Indo; 10−5 M), and the hyperpolarization blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA; 30 mM) for 15 min or endothelium denuded. Vascular segments were then precontracted with submaximal concentrations of Phe. Increasing concentrations (10−12–10−5 M) of E2, PPT, DPN, and G1 were then added, and the relaxation response was measured. Data represent means ± SE; n = 7–11 rats/group. *Significantly different (P < 0.05) from corresponding measurement in control nontreated intact vessels.