Figure 5. Role of P2Y1 purinoceptor in the development of longitudinal Ca2+ waves under shear stress .
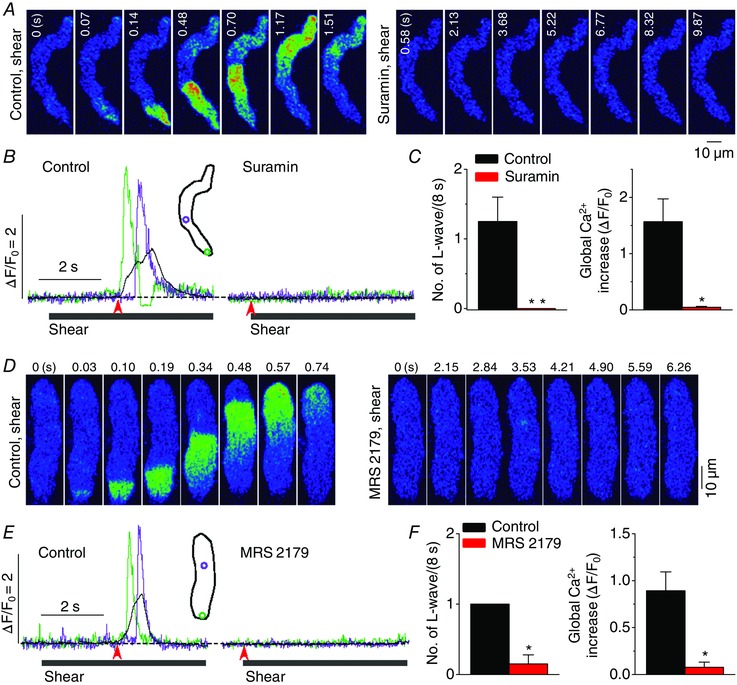
A and D, representative confocal Ca2+ images recorded during the applications of shear stress (∼16 dyn cm−2) in the absence (‘Control, shear’) and presence of the non‐selective inhibitor of P2 purinoceptor, suramin (10 μm; A, ‘Suramin, shear’), or the selective antagonist of P2Y1 receptor, MRS 2179 (0.2 μm; D, ‘MRS 2179, shear’). Both chemicals inhibited the occurrence of longitudinal Ca2+ wave under shear stress. B and E, changes in local (green and violet) and global (black) Ca2+ levels measured from the ROIs (inset) on the series of confocal Ca2+ images recorded in the cells shown in A (B) and D (E). The time marked by arrowheads matches with 0 s shown in the confocal images. C and F, summary of the effects of suramin (n = 6) and MRS 2179 (n = 8) on the occurrence of longitudinal Ca2+ waves and on global Ca2+ changes during the application of shear (8 s). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Control (paired Student's t test).
