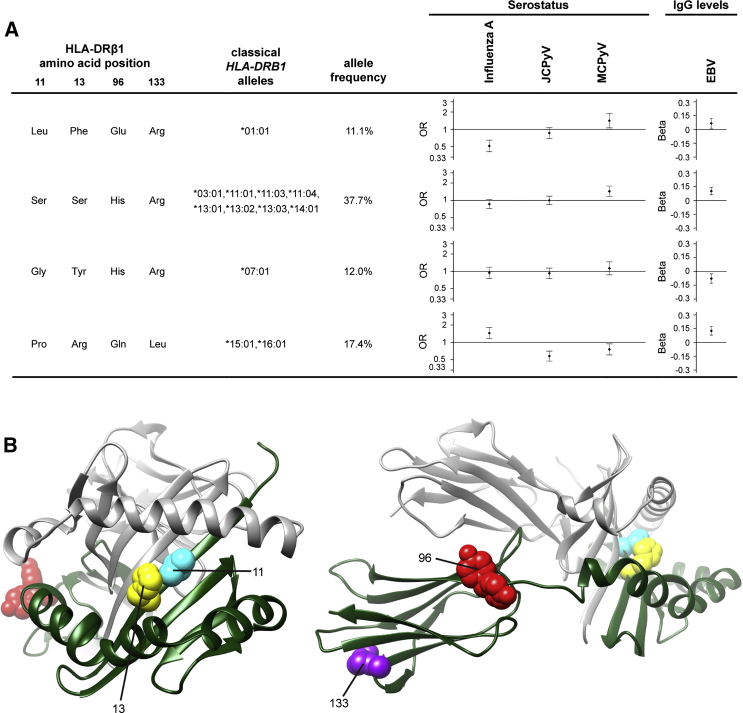
Figure 1.
Effect of Common HLA-DRβ1 Haplotypes on Virus Serostatus or Antibody Levels
(A) Estimated effects for HLA-DRβ1 haplotypes as defined by the strongest associated amino acid positions for influenza A virus, JCPyV, and MCPyV serostatus, as well as EBV IgG levels (Table 2). These four positions were imputed with SNP2HLA and all showed an imputation accuracy of > 99% in the original publication.13 The Val-His-Tyr-Arg-encoding haplotype with a frequency of 14.9%, present in classical HLA alleles HLA-DRB1∗04:01 and HLA-DRB1∗04:04, was chosen as reference (i.e., given an OR of 1, or a beta of 0, respectively) and not included in the figure. Only common haplotypes with a frequency of > 10% were included in the analysis and accounted for 93.1% of haplotype diversity. Diamonds designate estimated effect sizes; error bars define the 95% confidence interval. OR, odds ratio
(B) 3D model of the HLA-DR αβ heterodimer. The protein is shown in front (left) and side (right) views. The DR α chain is displayed in gray and the β chain in green. Associated amino acid positions, as selected for haplotype analysis, are highlighted. This figure was prepared with UCSF chimera,14 with Protein Data Bank code PDB: 4MCY.15