Figure 2.
Assembly of AP-4 Complexes by Variant ε Subunits
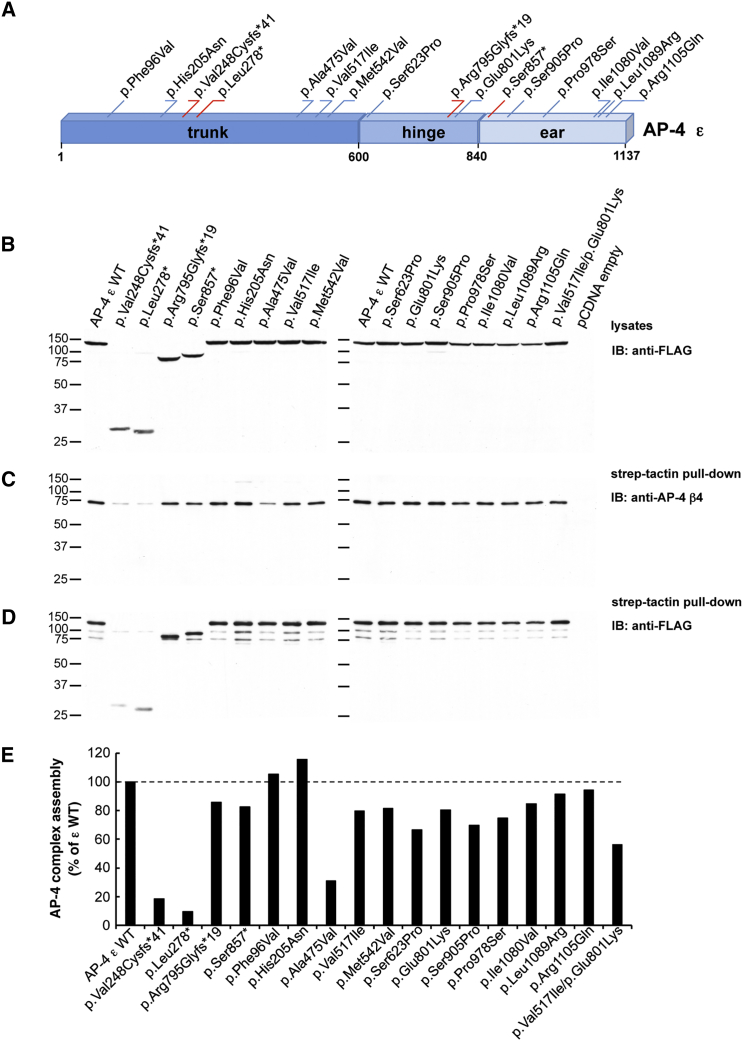
(A) Schematic representation of the AP-4 ε subunit. Single amino acid substitutions are indicated in blue, whereas truncating variants are depicted in red. The numbering corresponds to the human AP-4 ε isoform, comprising 1,137 residues (GenBank: NP_031373.2); assignment of domains is as in Boehm and Bonifacino.26
(B) Expression of wild-type (WT) and variant human AP-4 ε constructs tagged at their N termini with TSF-tagged ε constructs in HEK293T cells. Transfected cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibody.
(C) Assembly of WT and variant TSF-tagged ε constructs into AP-4 complexes. Lysates of transfected HEK293T cells were incubated with StrepTactin Sepharose beads. Pulled-down complexes were subsequently eluted with d-desthiobiotin and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-AP-4 β4 antiserum.16
(D) Immunoblot membranes with samples of the StrepTactin pull-down assays shown in (C) were stripped and subjected to additional immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibody.
(E) The assembly of AP-4 complexes by WT and variant ε constructs (pulled-down complexes detected by anti-β4; blots in C) was calculated in relation to the total expression of the cognate ε constructs in transfected HEK293T cells (blots in B). Blots were subjected to densitometric analysis with Image J software. Results are expressed as the percentage of assembly measured for WT ε (percentage of WT ε).