Figure 3.
The NAGPA Cytosolic Tail Interacts with μ Subunits of AP Complexes
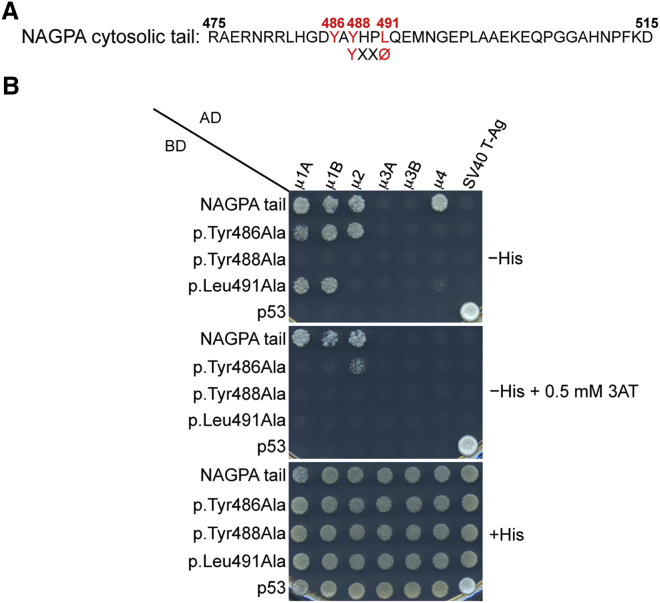
(A) Amino acid sequence of the human NAGPA cytosolic tail shows a YXXØ motif characteristic of endocytic and lysosome-targeting signals (X is any amino acid, and Ø is a bulky hydrophobic residue). Numbering corresponds to the isoform comprising 515 residues (UniProt: Q9UK23).
(B) Y2H analysis showed that the NAGPA cytosolic tail interacts with the μ subunits of AP-1 (both the μ1A and μ1B isoforms), AP-2, and AP-4. Interactions depend on residues Tyr488 and Leu491 in the YXXØ-based sequence of the NAGPA tail and on the Tyr486 residue located immediately upstream. The NAGPA cytosolic tail was subcloned in a Y2H Gal4 BD vector, whereas the AP μ subunits were subcloned in a Gal4 AD vector. Growth on the −His plates is indicative of interactions, whereas growth on the +His plate is a control for viability and loading of all double transformants. Co-transformation of the BD-NAGPA tail constructs with AD-SV40 T-Ag and of AD-μ subunits with the BD-p53 construct provided negative controls for the assay. Co-transformation of BD-p53 with AD-SV40 T-Ag provided a positive control for interactions. Plating on −His plates containing 0.5 mM 3-amino-1,2,4 triazole (3AT) provided an assay with increased stringency conditions (3AT is a competitive inhibitor of HIS3).