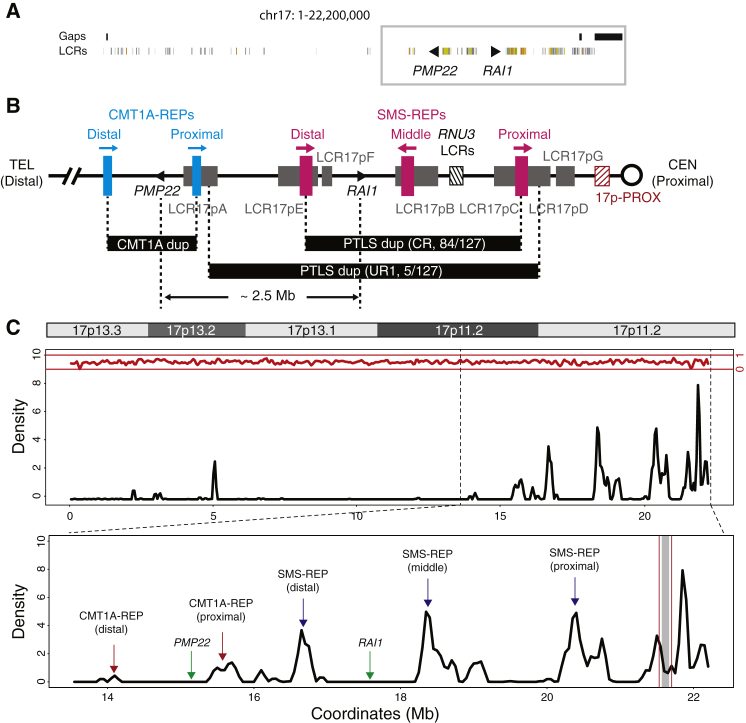
Figure 4.
Genomic Architecture in the Chromosome 17p Region
(A) Distribution of LCRs in chromosome 17p shown by the Segmental Dups track in the UCSC genome browser (hg19). Colored segments represent LCRs. Black triangles represent PMP22 and RAI1. Regions with gaps are shown as black segments on top of the LCR track. The gray box indicates proximal 17p region.
(B) LCR-rich genomic structure in the proximal 17p region. LCR clusters are shown by colored segments. Segments in blue, CMT1A-REPs; magenta, SMS-REPs; gray, LCR17pA-G; black hatched, RNU3 LCRs responsible for idic(17q); maroon hatched, 17p-PROX. The common recurrent CMT1A duplication, common recurrent (CR) and uncommon recurrent (UR1) PTLS duplications are shown as black segments between vertical dashed lines. Distance between PMP22 and RAI1 is approximately 2.5 Mb.
(C) LCR density plot in chromosome 17p region. The plot is based on the annotation in the Segmental Dups track from the UCSC Genome Browser. Top panel shows the ideogram of chromosome 17p. Middle panel is the LCR density plot showing the moving-average of LCR density along the chromosome 17p region. LCR density might be higher than 1 if multiple overlapping LCRs cluster in a given window. Density of other repetitive sequences from RepeatMasker is shown at the top in red. The bottom panel is zoom-in view of the middle panel focusing on the proximal 17p region. Major LCR clusters and genes are annotated. Region between vertical maroon lines indicate the 17p-PROX, and the region with gray shade represents the gap region in hg19, which is recently filled by satellite DNA sequences in hg38.