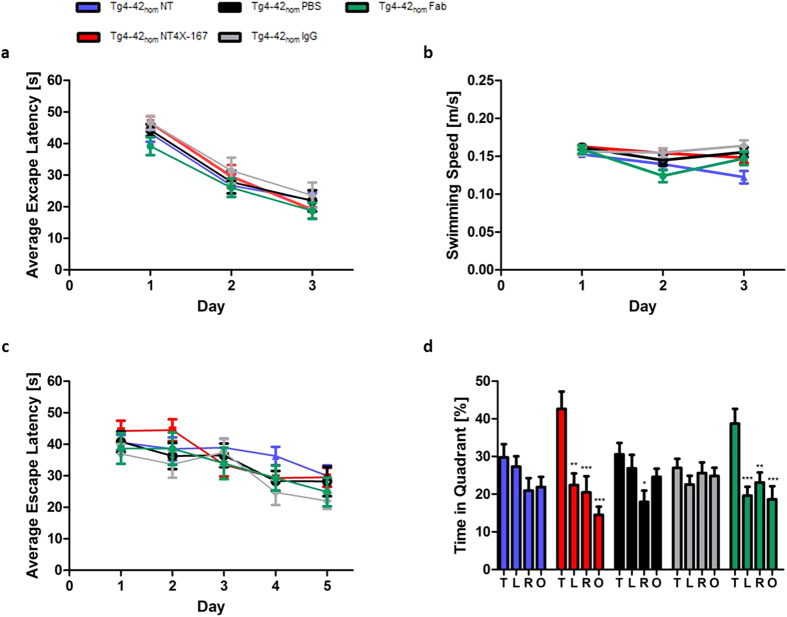
Figure 5. Passive immunization with NT4X rescues learning deficits in Tg4-42hom mice.
Tg4-42hom mice that received weekly injections with the full-length NT4X-antibody, the Fab fragment of NT4X, an IgG control antibody and PBS for a period of 12 weeks as well as a group of non-treated (NT) mice were tested at 6 months of age in the Morris Water Maze. (a,b) Cued training revealed that all mice exhibited intact eyesight and the motor abilities to perform the test. (a) Escape latency decreased progressively over 3 days of cued training for all mice. (b) Mice showed comparable swimming speeds. (c) Spatial learning was assessed in the acquisition training. All Tg4-42hom mice showed reduced escape latency over the 5 days of acquisition training. (d) Spatial reference memory was impaired in non-treated Tg4-42hom as well as in PBS- and IgG-treated Tg4-42hom mice as they showed no preference for the target quadrant in the probe trial. In contrast, Tg4-42hom mice immunized with the full-length NT4X and the Fab fragment of NT4X antibody displayed no learning deficits at this age. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05. n = 10–17 per group (Tg4-42hom NT: n = 17, Tg4-42hom NT4X: n = 15, Tg4-42hom Fab: n = 10, Tg4-42hom IgG: n = 14, Tg4-42hom PBS n = 15). Swimming Speed and escape latency: repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparisons. Quadrant preference: One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni multiple comparisons. T target quadrant, L left quadrant, R right quadrant, O opposite quadrant. Data presented as mean ± S.E.M; m = months.