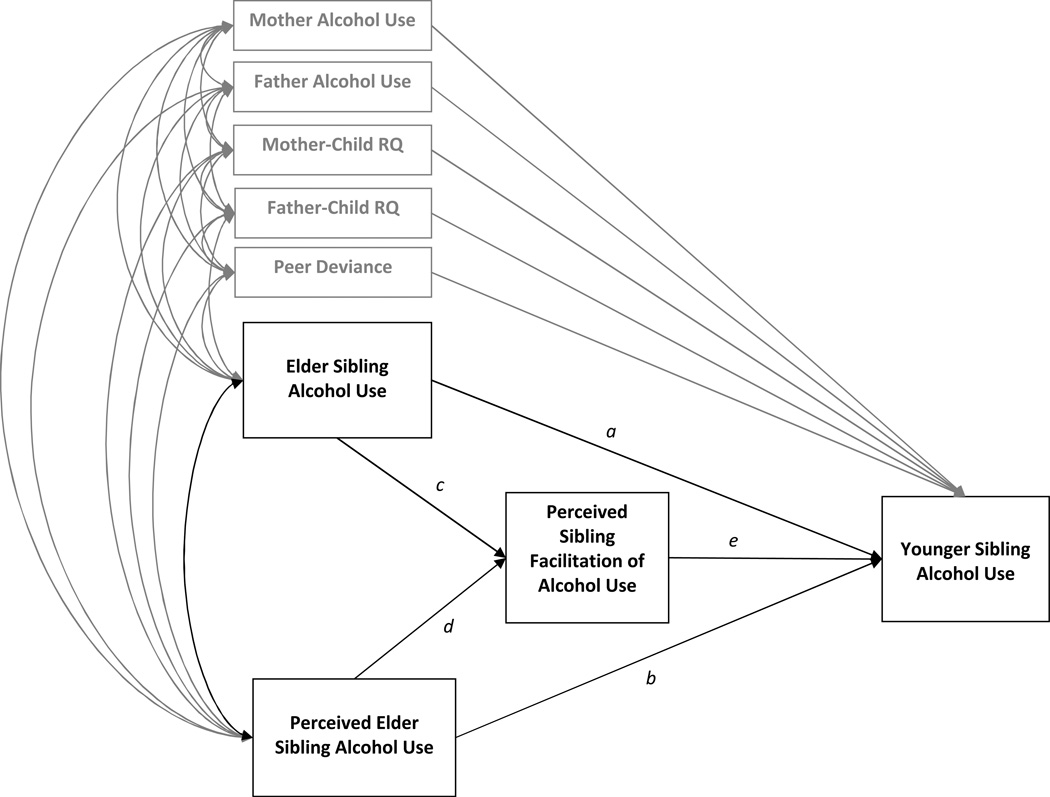
Figure 1. Conceptual Model Depicting Study Hypotheses.
RQ = Relationship Quality. Our goal was to evaluate a full mediation model of perceived sibling facilitation in the association between elder and younger sibling alcohol use (path a) and in the association between perceived elder sibling alcohol use and younger sibling alcohol use (path b), after controlling for parenting and peer influences (shown in gray for clarity of presentation). Direct associations are shown for paths a and b. Indirect associations are shown by paths c and e, and d and e. Significant coefficients for both direct and indirect effects suggest partial mediation. Significant indirect, but not direct coefficients, suggests complete mediation. To test for contextual influences, follow-up analyses examined moderation of all paths as a function of genetic relatedness (genetically related versus unrelated), sibling age difference (within 2 years, 2–3 years, 3+ years), sibling gender composition (same versus mixed), and shared ethnicity (same versus mixed).