Fig. 3.
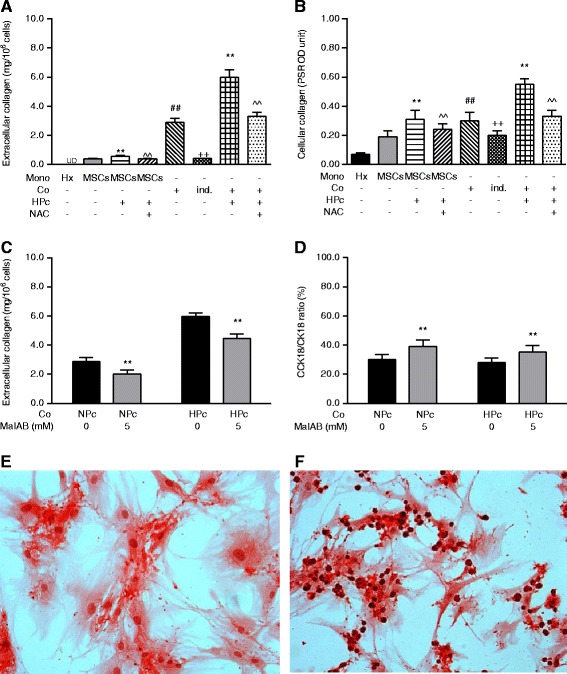
Dependence of co-culture hepatotrophic and HPc-induced potentiative effects on ROS-dependent MSC deposition of extracellular collagen. a Extracellular and b cellular collagen contents of mono-/co-cultured hepatocytes and NPc-/HPc-MSCs with or without NAC addition. c Inhibitory effect of MaIBA on extracellular collagen deposit of NPc- and HPc-MSCs. d Effects of 5 mM MaIBA pretreatment on main cellular death mode of hepatocytes co-cultured with NPc- versus HPc-MSCs. e and f Picro-sirius red staining (200×) for cellular and extracellular collagen of MSCs in mono-culture (left panel) and co-culture (right panel); nuclei are counterstained with hematoxylin. Values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). *p <0.05 and **p <0.01, versus control mono- or co-culture; ^^p <0.01, versus co-culture with HPc-MSCs; ## p <0.01, versus control mono-culture; ++ p <0.01, versus co-culture. CCK18 Caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18, CK18 Cytokeratin 18, Co Co-culture, HPc Hypoxia-preconditioned, Hx Hepatocyte mono-culture, ind. Indirect, MaIBA N-(methylamino)-isobutyric acid, Mono mono-culture, MSC Mesenchymal stem cell, NAC N-acetylcysteine, NPc Normoxia-preconditioned, PSR OD Picro-sirius red OD reading, UD undetectable
