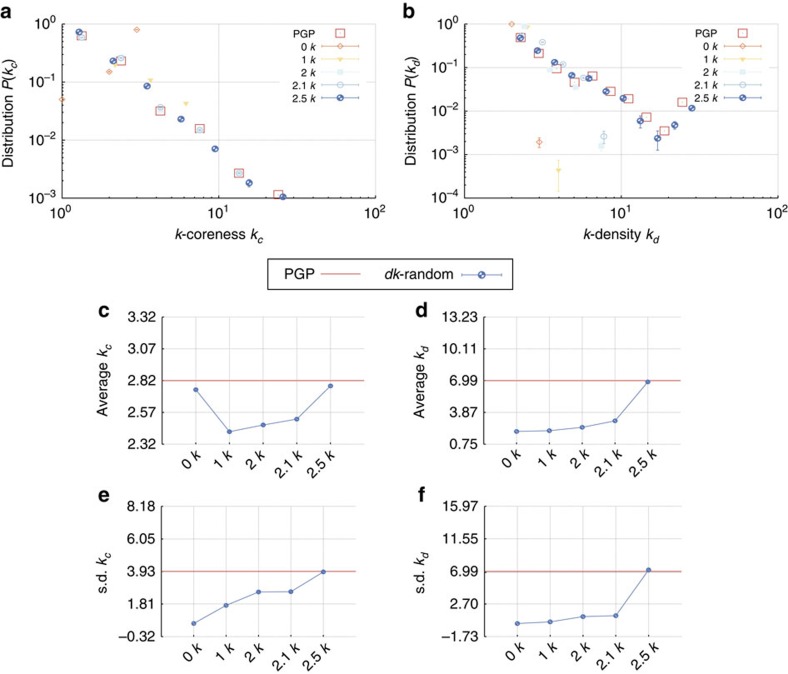
Figure 5. Mesoscopic properties, the k-coreness and k-density distributions, in the PGP network and its dk-random graphs.
The figure shows the distributions P(kc,d) of (a) node k-coreness kc and (b) edge k-density kd, and their (c,d) means and (e,f) s.d. The kc-core of a graph is its maximal subgraph in which all nodes have degree at least kc. The kd-core of a graph is its maximal subgraph in which all edges have multiplicity at least kd−2; the multiplicity of an edge is the number of common neighbours between the nodes that this edge connects, or equivalently the number of triangles that this edge belongs to. A node has k-coreness kc if it belongs to the kc-core but not to the kc+1-core. An edge has k-density kd if it belongs to the kd-core but not to the kd+1-core. The error bars indicate the s.d. of the metrics across different graph realizations.