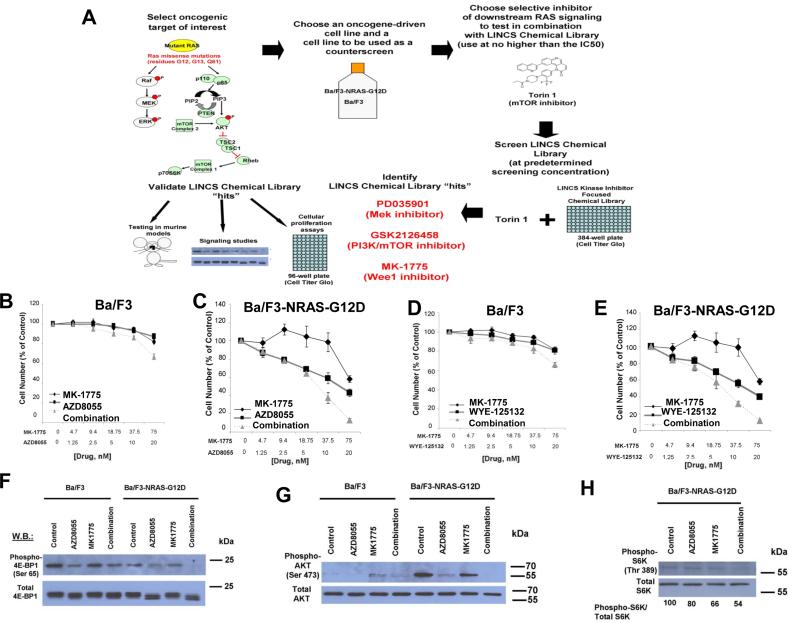
Figure 1. Identification of Wee1 inhibitor, MK-1775, as able to potentiate the effects of mTOR inhibition against mutant NRAS-expressing cells via inhibition of AKT, 4E-BP1, and S6K phosphorylation.
(A) Schematic of LINCS library chemical screen. 384-well plates were seeded with either parental Ba/F3 cells cultured in the presence of 15% WEHI (as a source of IL-3), which were used as a control to eliminate inhibitors that exhibit off-target toxicity and interfere with IL-3-mediated signaling, or Ba/F3-NRAS- G12D cells (growth factor-independent). Included in the screen were cell-containing plates that only received LINCS library drugs (300 nM, determined to be the optimal screening concentration) for the purpose of assessing single agent activity of the LINCS library compounds, or plates that contained LINCS library compounds (300 nM) plus the mTOR inhibitor, Torin 1 (20 nM, which was determined to be close to the IC50 against mutant NRAS-expressing cells). DMSO (vehicle) wells and Torin 1-only wells were included as controls in the plates. Following pintool administration of the library compounds, the 384-well plates were incubated for two days prior to administration of Cell Titer Glo (Promega, Madison, WI) and analysis of bioluminescence using a plate reader. Ideal candidates for further investigation were LINCS library compounds showing minimal activity as single agents against parental Ba/F3 cells, yet potentiation of the efficacy of Torin 1 against NRAS-driven cells. “Hits” were validated for synergizing potential using several approaches, including cellular proliferation assays, signaling studies, and in vivo analysis. (B-E) Approximately two-day proliferation studies performed with MK-1775, combined with AZD8055 or WYE-125132 against parental Ba/F3 and Ba/F3-NRAS-G12D cells. (F-H) Effect of approximately two-hr treatment of Ba/F3 or Ba/F3-NRAS-G12D cells with MK-1775 (75 nM), alone and combined with mTOR inhibitor, AZD8055 (20 nM), on phosphorylation of 4E-BP1, AKT, and S6K, as measured by immunoblotting.