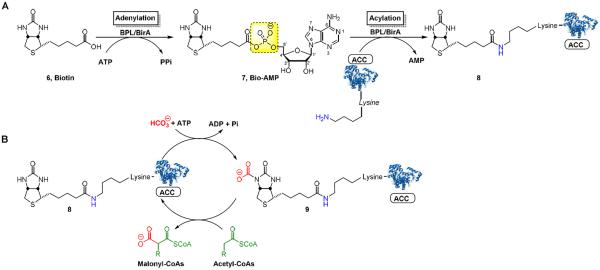
Figure 2.
(A) MtBPL catalyzed biotinylation of ACC, a biotin dependent enzyme proceeds in two steps by sequential adenylation of biotin (6) to form Bio-AMP (7) followed by acylation of the biotin carboxylase carrier protein domain of ACCs to furnish holo-ACC (8). (B) Biotinylated ACC proteins mediate carboxyl group transfer onto acyl-CoAs forming malonyl-CoAs for lipid biosynthesis. The N-1 atom of biotin is carboxylated in an ATP-dependent manner by the biotin-carboxylase domain of ACCs to furnish 9. In the second half-reaction, ACCs transfer the carboxy group onto an acyl-CoA, mediated by the biotin carboxylase domain of ACCs.