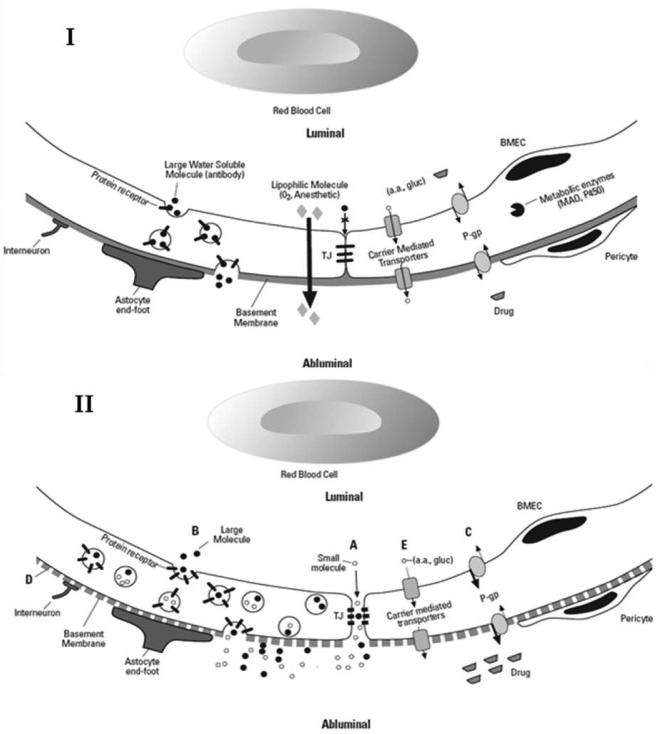
Figure 1. The Neurovascular Unit with normal and disrupted BBB.
(I) Functional barrier composed of transport systems and metabolic enzymes. The structural barrier includes tight junctions and basement membrane. (II) Disrupted BBB with (A) Increased paracellular permeability due to tight junction disruption (B) increased transcellular permeability via upregulated transcytosis (C) drug and toxin accumulation due to decreased efflux via P-gp (D) basement membrane disruption (E) decreased nutrient transport TJ = tight junctions, BMEC = brain microvascular endothelial cell, P-gp = permeability glycoprotein, a.a. = amino acids, gluc = glucose, MAO = monoamine oxidase inhibitor, P450 = drug metabolizing enzyme system