Figure 9.
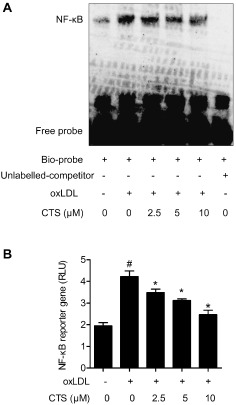
CTS inhibits oxLDL‐induced NF‐κB DNA binding and transcriptional activity in HUVECs. HUVECs were treated with CTS (2.5–10 μM) for 3 h followed by stimulation with oxLDL (80 μg mL−1) for 24 h. (A) Nuclear extracts (4 μg aliquots) were complexed with a biotin‐labelled NF‐κB probe and assayed for NF‐κB DNA binding activity by EMSA. The specificity of the binding was confirmed by cold competition experiments with a 100‐fold molar excess of unlabelled NF‐κB duplex oligonucleotide. The graph shows one representative experiment of five independent experiments. (B) Dual luciferase reporter assays were performed to evaluate the influence of CTS treatment on NF‐κB‐dependent transcriptional activity. Relative luciferase activity was calculated as the ratio of firefly luciferase activity to that of Renilla luciferase. n = 6. # P < 0.05 compared with untreated control group; *P < 0.05 compared with oxLDL‐treated group respectively.
