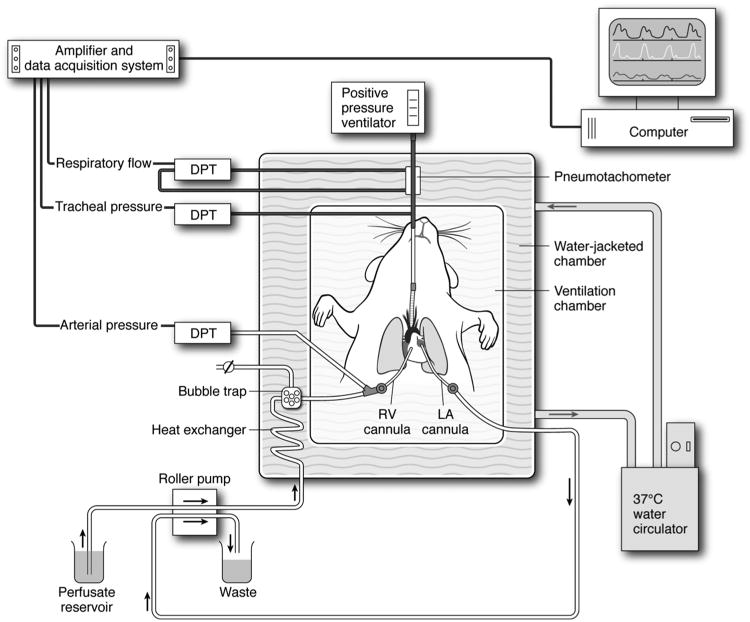
Figure 1. Diagram of the murine EVLP system.
An isolated, buffer-perfused mouse lung system (Hugo Sachs Elektronik, March-Huggstetten, Germany) was utilized. The right ventricular (RV) cannula is passed through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. A left atrial (LA) cannula drains perfusate into waste container. Lungs are perfused at a constant flow of 60 μl/g body wt/min. Lungs are ventilated with room air at 100 breaths/min at a tidal volume of 7 μl/g body weight with a positive end expiratory pressure of 2 cm H2O using a positive pressure ventilator. The perfusate and lungs are maintained at 37°C by use of a circulating water bath as shown. Air bubbles are removed from the perfusate via a bubble trap as shown. Several differential pressure transducers (DPT) and a pneumotachometer are used to measure arterial pressure, tracheal pressure and respiratory flow via the PULMODYN data acquisition system (Hugo Sachs Elektronik).