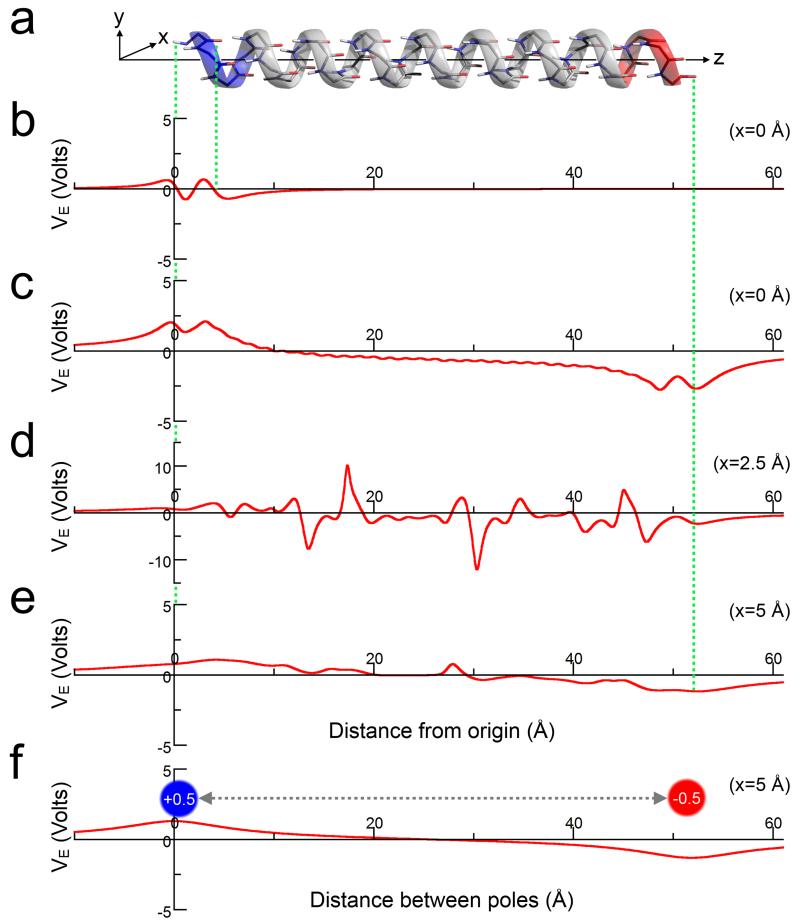
Figure 5. Electrostatic potential of a model α-helix.
(a) A 32-residue α-helix with its long axis aligned along z. (b) The electrostatic potential (VE) of a single residue from the helix at x = 0 Å. (c-e) The electrostatic potential along the entire helix at varying distances (x) from the helix axis: (c) x = 0 Å; (d) x = 2.5 Å; and (e) x = 5.0 Å. Note, the increased limits for the VE-axis in part (d). (f) The electrostatic potential arising from point charges of +0.5 and −0.5 at positions equivalent to the N- and C-terminal helical atoms on the z-axis, respectively. The electrostatic potentials in all parts (b-f) were calculated in vacuum.