Figure 1. DNA-Repair Pathways.
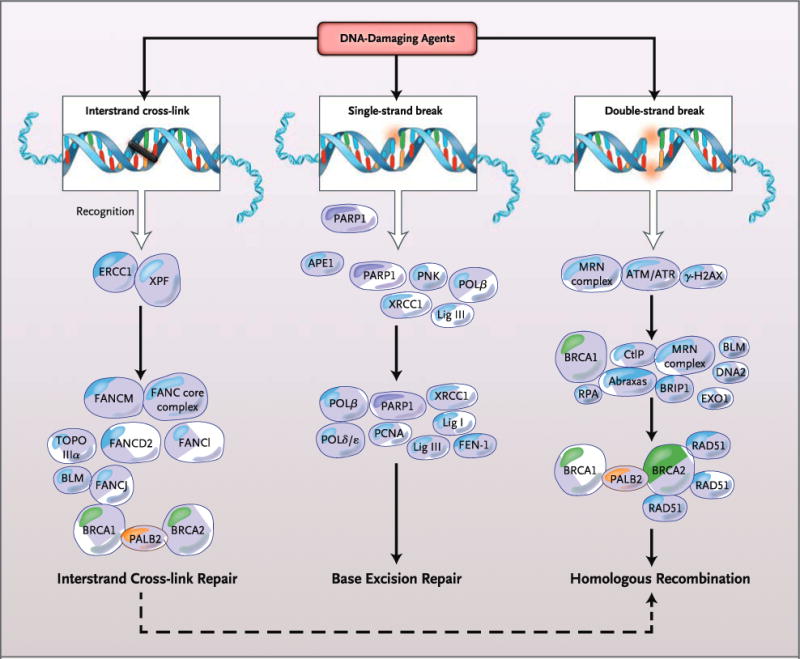
DNA damage from exogenous or endogenous sources may be repaired by a variety of DNA damage-response and damage-repair pathways, depending on the type of DNA damage induced. Interstrand cross-link repair, the single-strand-break repair subpathway of base excision repair, and homologous recombination address specific forms of damage with different, but in some cases common, proteins. The final step of interstrand cross-link repair involves homologous recombination. APE1 denotes apurinic-apirimidinic endonuclease 1; ATM ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR serine–threonine kinase; BLM Bloom’s syndrome, RecQ helicase–like; BRCA1 breast cancer 1, early onset; BRCA2 breast cancer 2, early onset; BRIP1 BRCA1-interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1; CtlP retinoblastoma binding protein 8; DNA2 DNA replication helicase/nuclease 2; ERCC1 excision repair cross-complementation group 1; EXO1 exonuclease 1; FANC core complex Fanconi’s anemia core complex; FANCM Fanconi’s anemia, complementation group M; FANCD2 Fanconi’s anemia, complementation group D2; FANCl Fanconi’s anemia, complementation group l; FANCJ Fanconi’s anemia, complementation group J; FEN-1 flap structure–specific endonuclease 1;·γ-H2AX phosphorylation of histone H2AX on serine 139; Lig I DNA ligase I; Lig III DNA ligase III; PALB2 partner and localizer of BRCA2; PARP1 poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; PCNA proliferating-cell nuclear antigen; PNK polynucleotide kinase; Polδ/ɛ DNA polymerase δ/DNA polymerase ɛ; Polβ DNA polymerase β; RAD51 RAD51 recombinase; RPA replication protein A; TOPO IIIα DNA topoisomerase IIIα; XPF xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group F; and XRCC1 x-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 1. The MRN complex is made up of Mre11, Rad50, and Nibrin.
