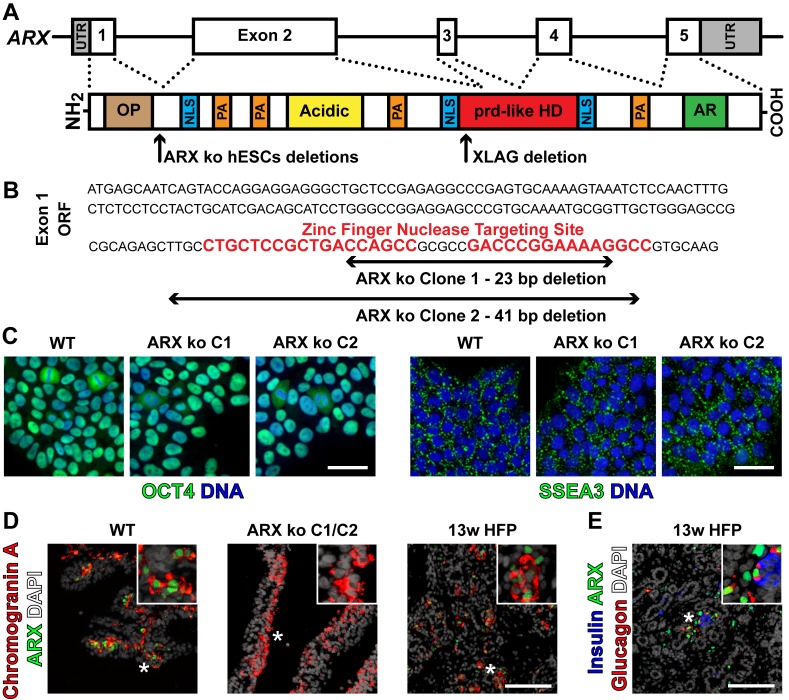
Fig 1. Generation of ARX ko hESCs.
(A) Schematic representation of the ARX gene and contained exons. Approximate protein domains and important functional regions of ARX including: octapeptide domain (OP), nuclear localization signals (NLS), poly-alanine expansion repeats (PA), Acidic domain (Acidic), prd-like homeodomain (prd-like HD), and Aristaless domain / C-peptide (AR). Approximate location of zinc finger nuclease mediated genomic editing induced deletion mutations in ARX knockout (ARX ko) hESCs and naturally occurring mutation of the XLAG pancreatic sample used in this study are also depicted. (B) Specific nucleotide deletions of ARX surrounding the high-specificity 36 bp ZFN recognition sequence within exon 1. ARX ko hESCs clones resulted in a frameshift mutation and premature stop codons in ARX. (C) Wild type (WT) and ARX ko clones 1 and 2 immunostained for pluripotency associated markers OCT4 (green) or SSEA3 (green) and counterstained for DNA with Hoechst 33342. Scale bar is 50 μm. (D) Immunostaining of ARX protein in agarose-embedded sections of 26-day differentiated WT or ARX ko pancreatic cells as well as human fetal pancreatic tissue at 13 weeks of gestation (13w HFP); ARX (green), chromogranin A (red), and DAPI (white). (E) 13w HFP immunostained for ARX (green), insulin (blue), glucagon (red), and DAPI (white) showing natural ARX expression patterns. Inset is a ~3x enlarged portion from the region indicated by the star. Scale bar for D and E is 100 μm.