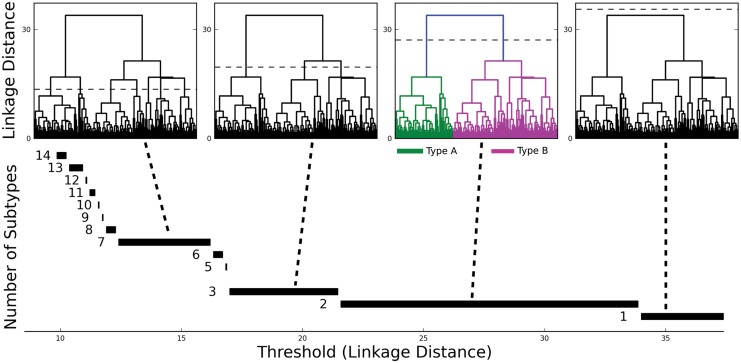
Fig 4. Two main types of pyramidal neurons in turtle dorsal cortex.
(TOP) Ward’s unsupervised clustering applied to a sample of 225 pyramidal neurons from turtle dorsal cortex, with each neuron characterized by 14 electrophysiological parameters. The x-axis in each plot represents the individual neurons. The y-axis represents the Euclidean distance between the two merged neurons/clusters in parameter space. Dashed lines in the four identical dendrograms indicate possible threshold choices. The dashed line in the colored dendrogram marks the threshold as suggested by the Thorndike procedure, which indicates two types of pyramidal neurons. (BOTTOM) The number of types increases with decreasing threshold in units of the linkage distance. The most robust choice of the threshold value is suggested by the widest range of threshold values in normalized parameter space for which the number of pyramidal neuron types is constant. This choice also indicates two main types of pyramidal neurons in turtle dorsal cortex.