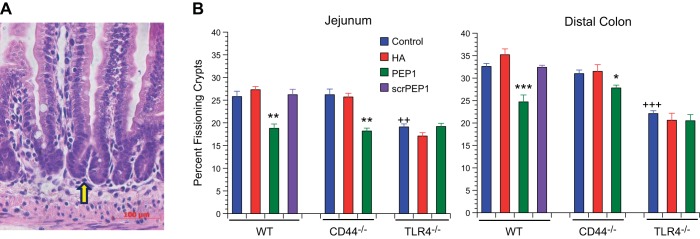
Fig. 4.
Effect of genotype and treatment with HA or PEP-1 on crypt fission in 14-day-old mice. A: H and E-stained histologic section of 14-day-old WT mouse small intestine showing a fissioning crypt (arrow). Scale bar = 100 μm, original magnification ×200. B: effect of genotype was measured; TLR4−/− genotype in postnatal mice affects baseline crypt fission. 14-day-old TLR4−/− control mice had a baseline frequency of crypt fission that was significantly reduced in the small intestine (20%) and colon (22%) compared with 14-day-old WT control intestine (26%) and colon (33%). In 14-day-old CD44−/− mice, baseline frequencies of crypt fission in the intestine (26%) and colon (31%) were the same as in 14-day-old WT controls. ++P < 0.001, +++P < 0.0001 compared with WT control. Effect of treatment was measured; intraperitoneal administration of exogenous HA from age 7 days to age 14 days had no effect on the frequency of crypt fission in small intestine or colon in WT, CD44−/−, or TLR4−/− mice. Blocking endogenous HA by intraperitoneal administration of PEP-1 using the same regimen resulted in a significant reduction of intestinal and colonic crypt fission in WT and CD44−/− mice but had no effect on crypt fission in TLR4−/− mice. Values are means ± SE for 9 mice per treatment group. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001 compared with control of the same genotype.