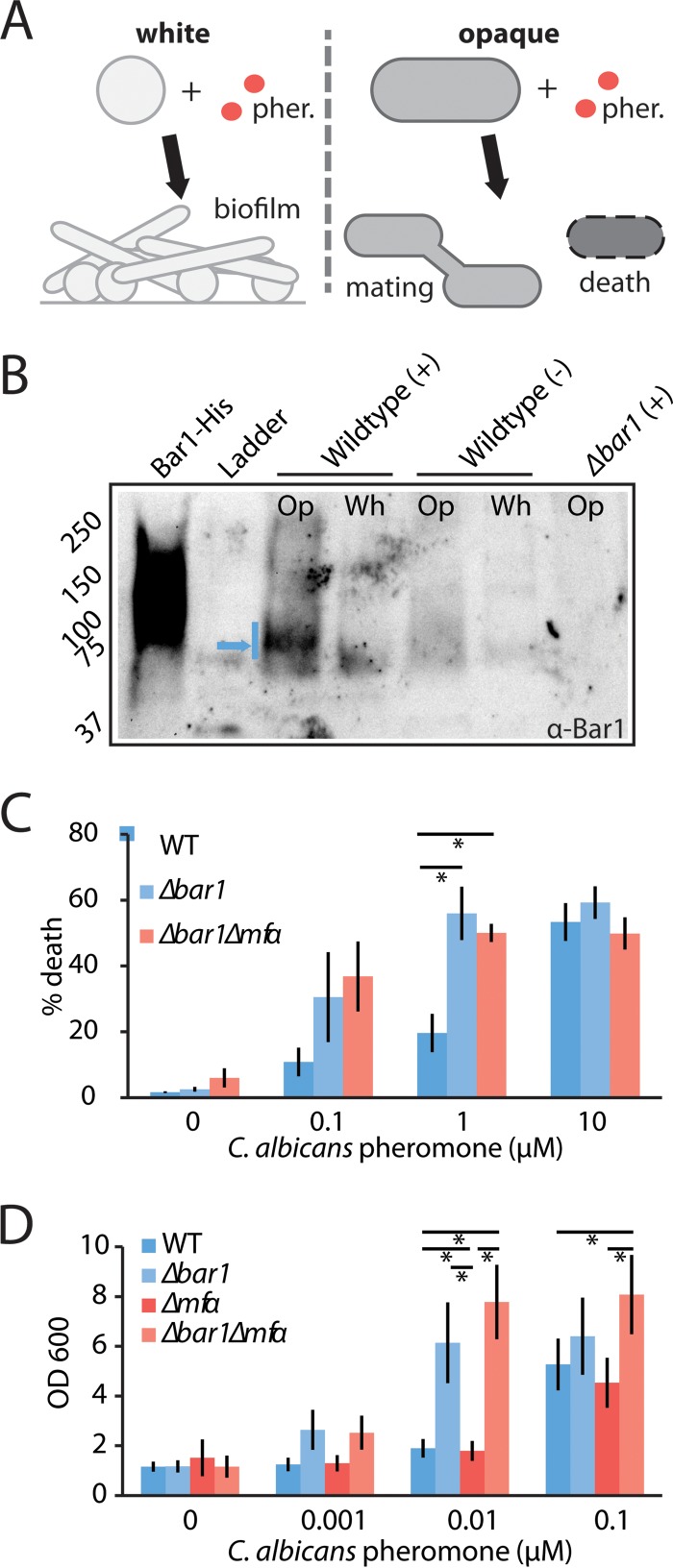
FIG 5 .
Analysis of the role of C. albicans BAR1 on the pheromone response in white and opaque MTLa cells. C. albicans wild-type, bar1Δ/bar1Δ, and bar1Δ/bar1Δ mfαΔ/mfαΔ MTLa strains were compared for their responses to α pheromone. (A) Schematic indicating pheromone (pher.) responses of C. albicans white and opaque a cells. White cells become adherent and form biofilms, whereas a fraction of opaque cells experience cell death. (B) Secretion of Bar1 by white (Wh) or opaque (Op) MTLa cells. Cells were exposed to a vehicle control (−) or 0.3 µM α pheromone (+) for 5 h, and Bar1 protein was detected from the supernatant via Western blotting using an anti-Bar1 antibody. Recombinant Bar1-His protein is used as a positive control, and bar1Δ/bar1Δ opaque cells are used as a negative control. Blue arrow, dominant Bar1 band. (C) Evaluation of gene function in opaque MTLa cells. A pheromone-induced death (PID) assay was used to assess the response of opaque a cells to α pheromone. Cells were treated with the indicated amount of α pheromone for 5 h and stained with propidium iodide, and the percentage of death was determined by flow cytometry. Error bars indicate standard errors (SE). (D) Evaluation of gene function in white MTLa cells. A biofilm assay was used to assess the response of white cells to α pheromone. Cells were incubated with α pheromone for 2 days, and adherent cells were quantified using absorbance at 600 nm. Error bars indicate SD. *, P < 0.05 by t test.