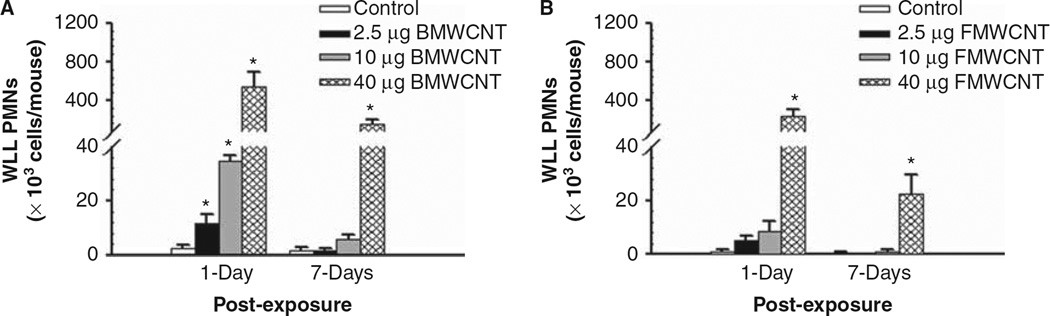
Figure 1.
Comparison of inflammation induced by pharyngeal aspiration exposure to 0, 2.5, 10 and 40 µg/mouse of BMWCNT (A) and FMWCNT (B) at 1 and 7 days post-exposure. WLL PMNs were used as a marker of pulmonary inflammation. Values are given as means ± SE (n = 8). An asterisk (*) indicates that PMN influx for that group were significantly higher than control (p < 0.05).