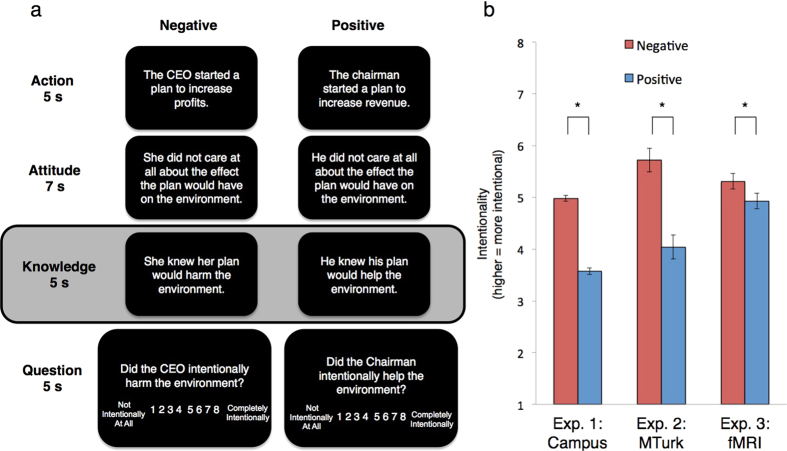
Figure 1. Asymmetries in intentionality are robust across three different methods of experimentation.
(a) In the fMRI version of the task, participants read and responded to two versions of each general story. These versions differed in whether the agent’s actions lead to morally negative or positive consequences (40 pairs for 80 vignettes total). Participants provided ratings of intentionality on a scale from 1 (Not Intentionally at All) to 8 (Completely intentionally), and the direction of the scale was counterbalanced trial-by-trial. Reported imaging results are derived from data collected during the “Knowledge” epoch. The ITI was 2 s. (b) At the group level, participants consistently rated actions in negative conditions as being more intentional than those in positive conditions across three different experiments. Model-free means are presented along with 95% confidence intervals for comparison across three different experimental designs. *Indicates that the means are different according to paired t-tests.