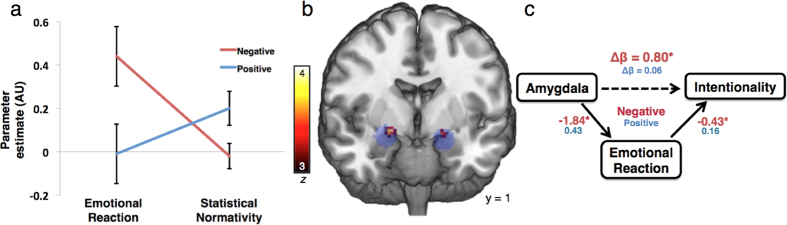
Figure 2. Converging behavioral and neural evidence suggests that Ascription leads to higher intentionality through an emotional mechanism while Denial leads to lower intentionality and is dependent on statistical normativity.
(a) Behaviorally, emotional reaction significantly predicts intentionality ratings for negative conditions but not for positive conditions. Conversely, statistical normativity predicts intentionality ratings for positive conditions but not for negative conditions. The parameter estimates and 95% confidence intervals are presented from the hierarchical, mixed-effects model. (b) Activation in bilateral dorsal amygdala (red-yellow colormap) was found to be positively associated with intentionality ratings for negative outcomes within ROIs identified from reverse inference maps of “emotion” from Neurosynth, indicated in blue66,67. (c) This relationship was partially mediated by reports of emotion for negative consequences (Indirect Effect Estimate (Δβ) = 0.80; 95% confidence interval = [0.07, 2.02]) while reports of positive emotion did not have a mediating role (Supplementary Table 4). Emotional reaction ratings are presented on a valenced scale, such that negative values indicate stronger negative emotional responses. β for separate negative and positive consequence mediation models are indicated, while the Δβ indicates the change in beta value for the direct path after controlling for the indirect path.