Figure 2. Intrinsic membrane properties of the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons are comparable to those of endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells.
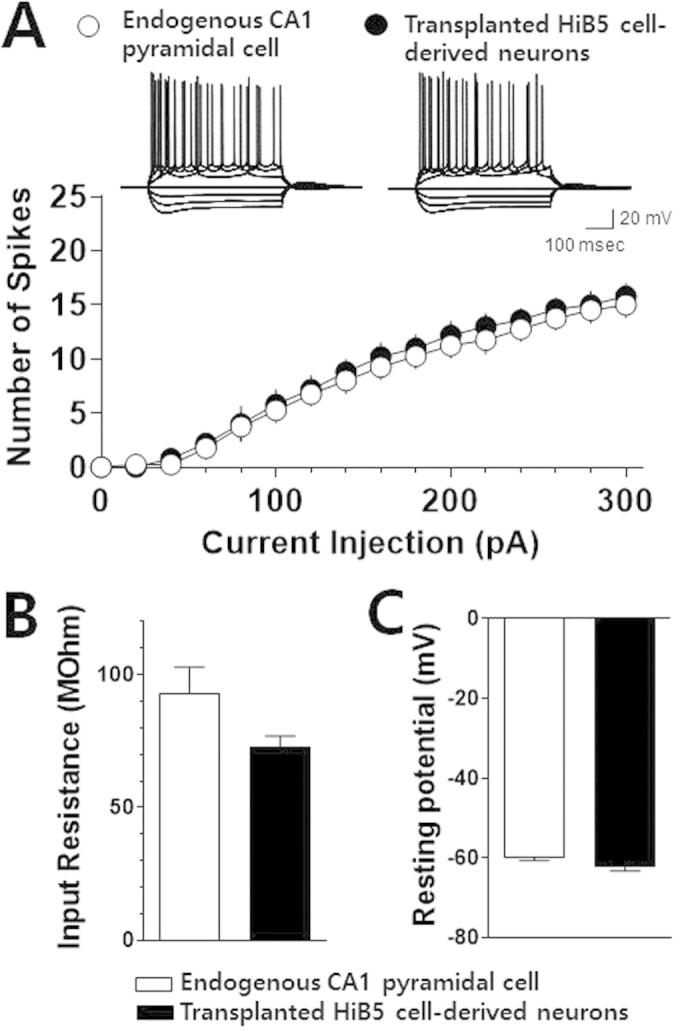
(A) Action potentials in the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons and endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells. Inset shows representative recording traces in a current-clamp mode elicited by current steps from HiB5 cell-derived neurons and endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells. The current steps were from −300 pA to +300 pA in +100-pA increments. Graph shows average numbers of action potentials evoked by a series of depolarizing current steps from the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons and endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells. Values are mean ± SEM. (B) Input resistance in the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons and endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells. 92.98 ± 9.77 MΩ for HiB5 cell-derived neurons, n = 5; 72.68 ± 4.23 MΩ for endogenous pyramidal cells, n = 4; P > 0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test. (C) Resting membrane potential in the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons and endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells. –62.28 ± 0.96 mV for HiB5 cell-derived neurons, n = 5; –59.95 ± 0.66 mV for endogenous pyramidal cells, n = 4; P > 0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test.
