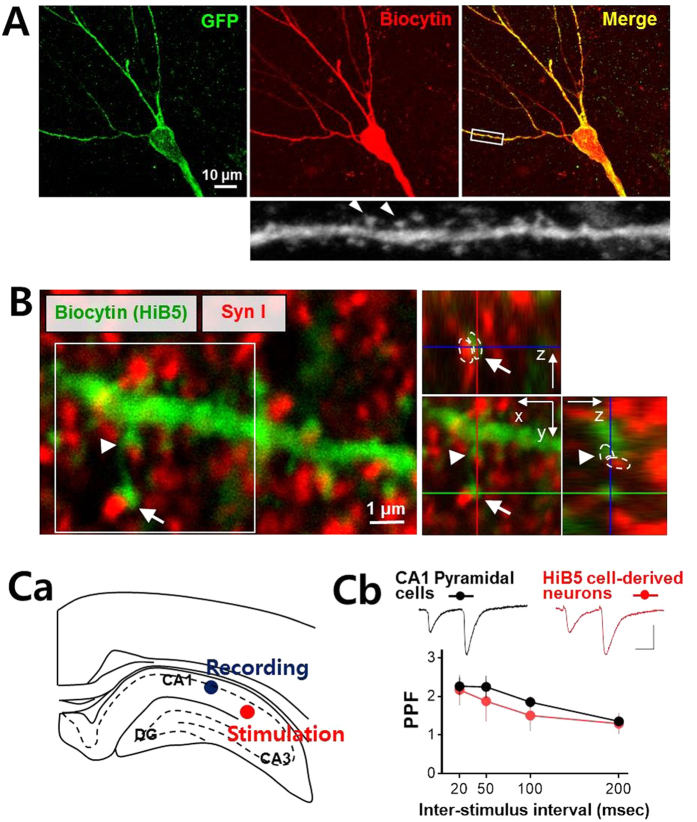
Figure 3. Implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons functionally integrate into hippocampal neural circuits.
(A) Dendritic architecture of the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons in CA1. Recorded HiB5 cell-derived neurons were retrospectively visualized by immunofluorescence staining for GFP (green) and biocytin (red). Mushroom-shaped dendritic spines (arrow heads) were clearly seen in the enlargement of the secondary dendrite boxed in the merged image. (B) Apposition of biocytin-positive spines of the HiB5 cell-derived neurons (green) and synapsin I-positive presynaptic terminals (red). The z-stack reconstruction of the boxed area clearly demonstrates the synapse formation on dendritic spines of the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons (arrow and arrowhead). (C) Paired-pulse facilitation at synapses in the HiB5 cell-derived neurons. Ca illustrates stimulation and recording sites in coronal brain slices. Synaptic responses were evoked in neurons in CA1 pyramidal layer by stimulation of Schaffer collateral pathway. Cb shows paired-pulse ratio (PPR, EPSC2/EPSC1) from the endogenous CA1 pyramidal cells and the implanted HiB5 cell-derived neurons. The insets show representative electrophysiological traces averaged 5 consecutive EPSCs evoked by paired pulses (50 ms inter-stimulus interval) in an endogenous CA1 pyramidal cell and a implanted HiB5 cell-derived neuron (scale bars: 25 ms and 50 pA).