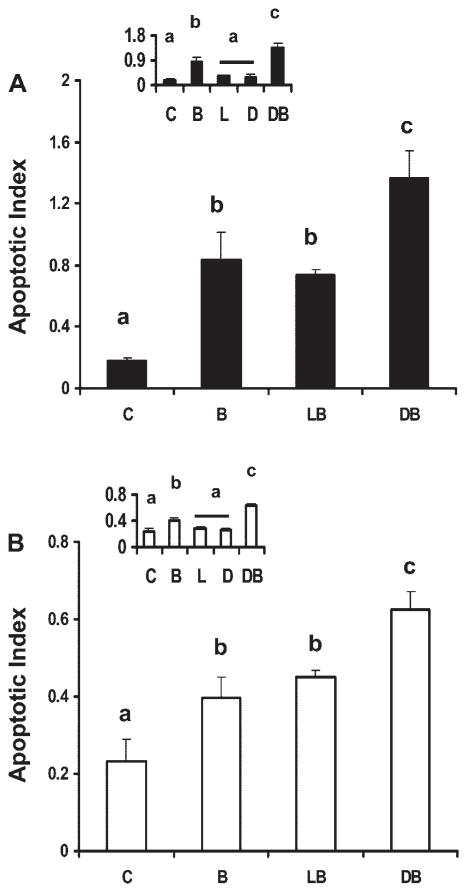
Fig. 1.
Effect of fatty acid and butyrate cotreatment on apoptosis in p53 wild-type and knockout cells. p53 Wild-type (p53+/+, solid bars; A) and p53 knockout (p53−/−) cells (open bars; B) were treated with fatty acid (50 μM) for a total of 72 h and 0 or 5 mM butyrate for the final 12 h. Insets show fatty acid-only treatment effects compared with control treatment groups, from independent experiments. Nonadherent cells were harvested and apoptosis was measured by the nucleosomal fragmentation release assay. Data are means ± SE from a representative experiment, n = 6–8 wells per treatment. Control cultures (insets) containing no treatment (C), butyrate only (B), linoleic acid (LA) only (L), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) only (D), LA and butyrate (LB), DHA and butyrate (DB). Data demonstrate that DB significantly enhanced apoptotic index compared with the other treatment groups whereas fatty acid only had no effect. Bars not sharing a common letter are significantly different at P < 0.05.