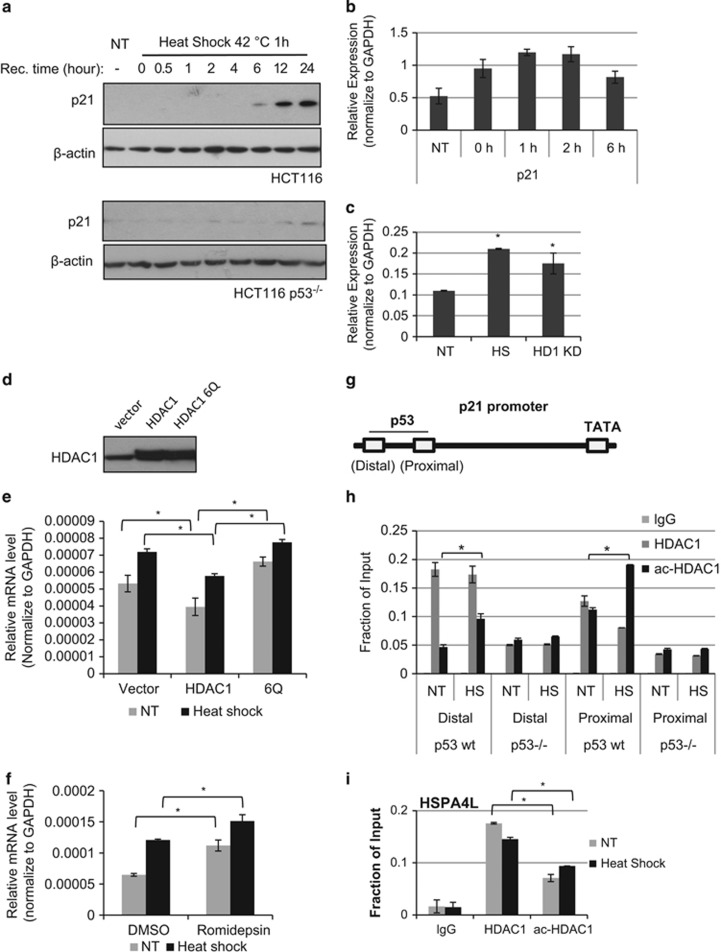
Figure 5.
Dynamic HDAC1 acetylation regulates p21 promoter activity in response to cell stress. (a) HCT116 cells or p53 null HCT116 cells were subjected to heat shock at 42 °C for 1 h and then recovered at 37 °C for an indicated time period. P21 protein levels were determined by western blot. (b) HCT 116 cells were subjected to heat shock for 1 h and recovered for indicated period of time. p21 mRNA level was tested by RT qPCR. (c) P21 mRNA level was tested by RT-qPCR from HCT116 extracts with heat-shock treatment or HDAC1 knock down. The heat shock was performed at 42 °C for 1 h and then recovered at 37 °C for 8 h. P21 mRNA expression is shown relative to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (mean±S.E.). *Significant difference compared to the non-treatment (NT) cells (P<0.05 by Student's t-test). (d) HDAC1 and acetyl-mimic mutant 6Q were transfected into HCT116 cells and HDAC1 levels were determined by Western blot. (e) The p21 expression level was determined from cells overexpressed with HDAC1 or 6Q and treated with heat shock. The relative p21 levels were normalized to GAPDH (mean± S.E.). The extracts were prepared 8 h after recovered at 37 °C. *Significant difference compared with vector control cells (P<0.05 by Student's t-test). (f) HCT116 cells were treated by 20 μM Romidepsin or DMSO and then subjected to heat shock. After 8 h of recovery, the p21 mRNA level was tested by RT-qPCR. The relative p21 levels were normalized to GAPHD (mean±S.E.). NT, non-treatment control compared with heat-shock treatment. *Significant difference compared with DMSO NT control cells (P<0.05 by Student's t-test). (g) P21 enhancer region with marked two p53 binding sites and TATA region. (h) ChIP assay for HDAC1 and acetylated HDAC1 in HCT116 wild-type and p53-null cells. The cells were subjected to heat shock at 42 °C for 1 h and then recovered at 37 °C for 2 h. The precipitated DNA was subjected to real-time PCR with primers amplifying p21 enhancer regions. *Significant difference compared with untreated control (P<0.05 by Student's t-test). (i) ChIP assay for HDAC1 and acetylated HDAC1 in HCT116 cells. The cells were subjected to heat shock at 42 °C for 1 h and then recovered at 37 °C for 2 h. The precipitated DNA was subjected to real-time PCR with primers amplifying HSPA4L gene promoter regions. *Significant difference (P<0.05 by Student's t-test)