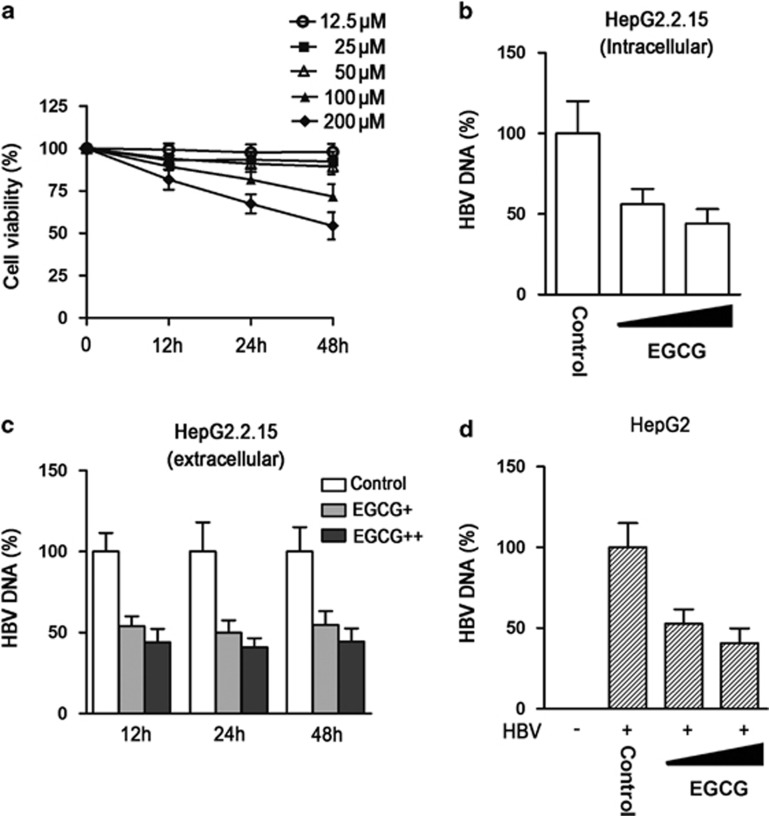
Figure 2.
EGCG inhibits HBV replication. (a) The effect of EGCG on the viability of HepG2.2.15 cells. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with increasing amounts of EGCG (12.5, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μM) for the indicated time points (0, 12, 24, and 48 h). The cell viability was determined by CCK-8 method, bars represent means±S.E.M (n=3). (b) The effect of EGCG on intracellular HBV DNA level in HepG2.2.15 cells. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with 25 or 50 μM of EGCG for 24 h, and the HBV DNA level in the cell lysates were determined by real-time PCR, bars represent means±S.E.M (n=3). (c) The effect of EGCG on extracellular HBV DNA level in HepG2.2.15 cells. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with 25 or 50 μM of EGCG for 24 h, and the HBV DNA level in the cell supernatants were determined by real-time PCR, bars represent means±S.E.M (n=3). (d) The effect of EGCG on HBV replication in HepG2 cells. HepG2 were transfected with pHBV1.3. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, cells were treated with 25 or 50 μM of EGCG for 24 h. The level of HBV DNA was determined as in panel (b)