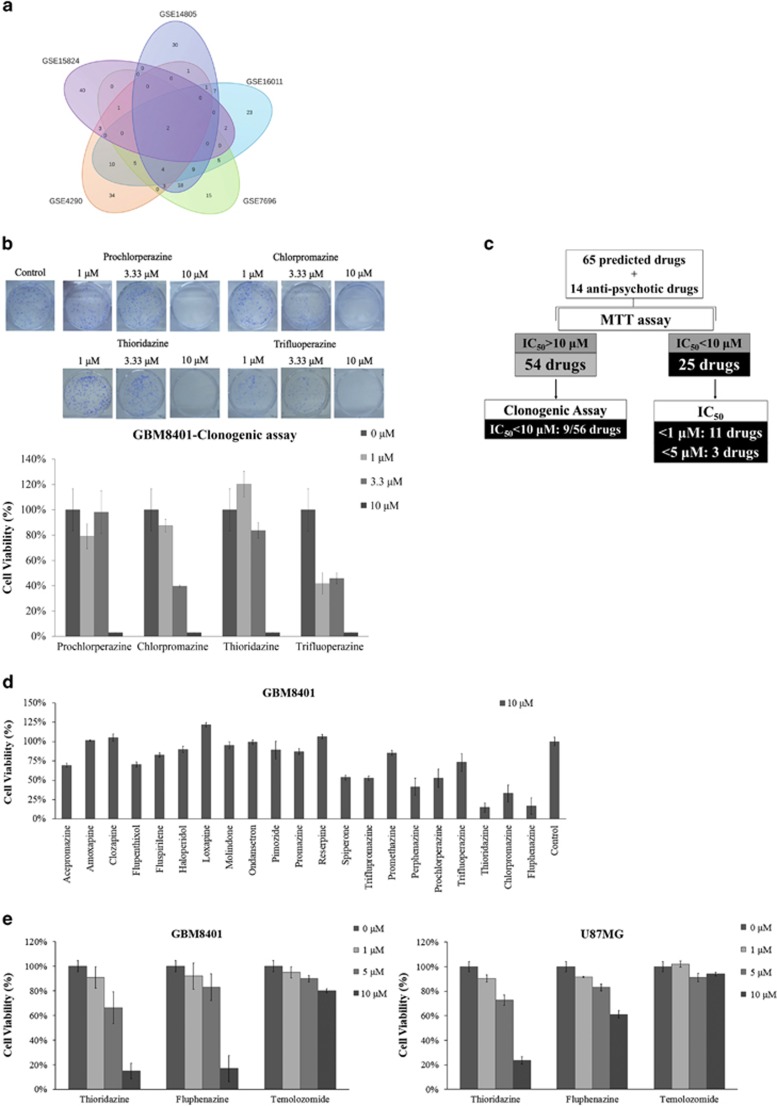
Figure 1.
Integrated bioinformatics and biochemical analyses reveal potential drugs for GBM. (a) This Venn diagram represents the number of drugs found using the five GBM data sets used to query the Cmap database. (b) GBM8401 cells were treated with prochlorperazine, chlorpromazine, thioridazine and trifluoperazine at concentrations ranging from 1 to 10 μM, and cell viability was determined using a clonogenic assay. (c) Summary of drugs tested on GBM8401 cells. Of the 215 potential GBM drugs as predicted by Cmap, we randomly selected 65 potential drugs and 14 antipsychotic drugs based on the availability of well-known scientific names and manufacturers, and we tested the cytotoxicity of these drugs in two GBM cell lines via an MTT and/or a clonogenic assay. There were 25 effective drugs (IC50<10 μM) in the MTT assay and 9 drugs effective (IC50<10 μM) in the clonogenic assay. (d) GBM8401 cells were treated with 10 μM various antipsychotic drugs for 72 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. (e) GBM8401 and U87MG cells were treated with thioridazine, fluphenazine or temozolomide (the only FDA-approved drug for GBM) at concentrations of 1, 5 or 10 μM for 72 h, respectively. Cell viability was determined via MTT assay