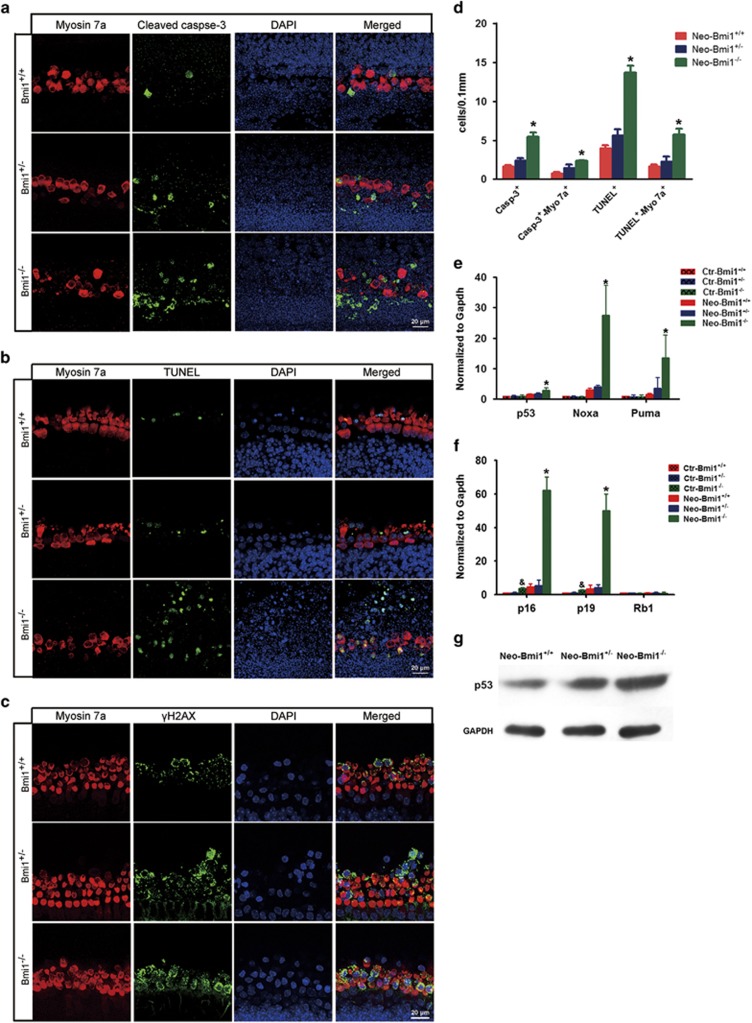
Figure 4.
Apoptosis and DNA damage in hair cells was augmented in Bmi1−/−cochlear epithelium after neomycin insult. (a) Cleaved caspase-3 and myosin 7a double staining in Bmi1−/−, Bmi1+/− and Bmi1+/+ cultured cochlear epithelium after neomycin treatment for 8 h. Middle turn. (b) TUNEL and myosin 7a double staining in Bmi1−/−, Bmi1+/− and Bmi1+/+ cultured cochlear epithelium after neomycin treatment for 8 h. Middle turn. (c) γH2AX and myosin 7a double staining in Bmi1−/−, Bmi1+/− and Bmi1+/+ cultured cochlear epithelium after neomycin treatment for 8 h. Middle turn. (d) Statistical data revealed that the number of cleaved caspase-3+/myosin 7a+ and TUNEL+/myosin 7a+ cells significantly increased in Bmi1−/− hair cells when compared with WT controls. (e and f) Real-time RT-PCR data showed the mRNA levels of p53, Noxa, Puma, p19, p16 and Rb1 after neomycin damage for 12 h. (g) Western blotting results showed the protein levels of p53 increased in Bmi1−/− cochlear epithelium after neomycin damage for 12 h. Scale bars: 20 μm. *P<0.05 versus Neo-Bmi1+/+ group. &P<0.05 versus Ctr-Bmi1+/+ group. n=5 for each group