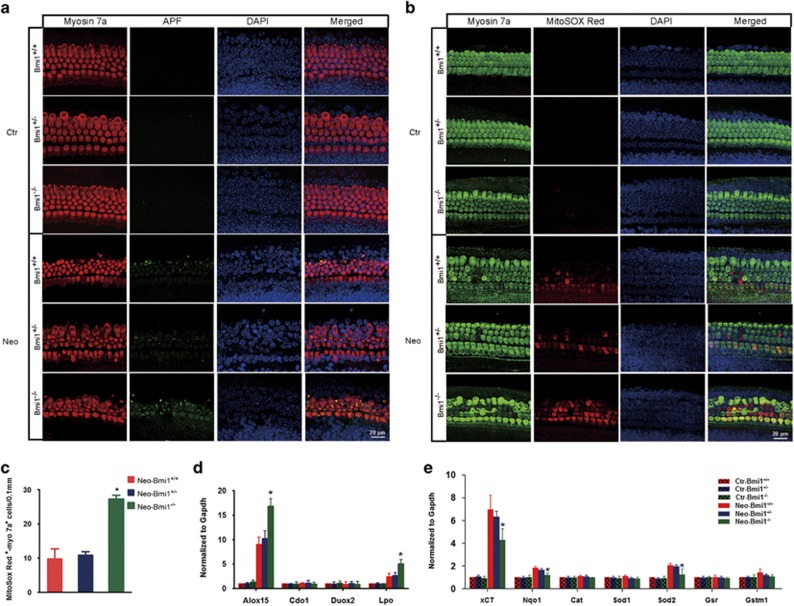
Figure 5.
The level of ROS increased and the disequilibrium of antioxidant–prooxidant balance deteriorated in Bmi1−/− hair cells after neomycin insult. (a) In the absence of damage, APF fluorescence in cochlear epithelium could not be detected. Two hours after 0.25 mM neomycin treatment, APF fluorescence is obviously stronger in hair cells of Bmi1−/− mice compared with that in WT and Bmi1+/− mice. Middle turn. (b) In the absence of damage, MitoSox Red fluorescence in cochlear epithelium could not be detected. Two hours after 0.25 mM neomycin treatment, MitoSox Red fluorescence is obviously stronger in hair cells of Bmi1−/− mice, compared with that in WT and Bmi1+/− mice. Middle turn. (c) Statistical data revealed that the number of MitoSox Red+/myosin 7a+ cells significantly increased in Bmi1−/− hair cells when compared with WT controls. Quantitative data showed the expression level of antioxidant genes (d) and oxidases (e) at 2 h after neomycin treatment. Scale bars: 20 μm. *P<0.05 versus Neo-Bmi1+/+ group. n=5 for each group