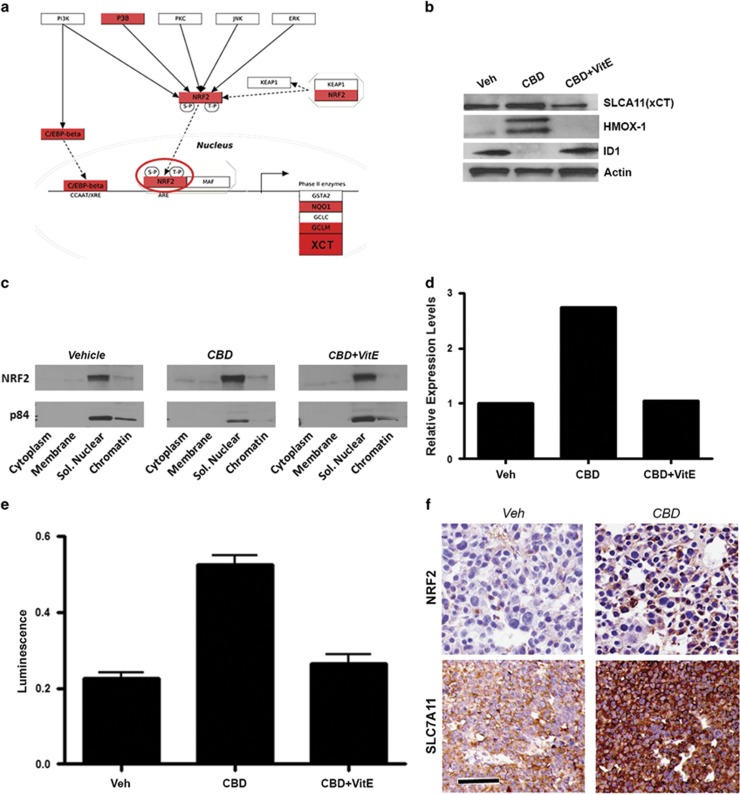
Figure 5.
CBD induces nuclear translocation and activation of NRF2 and its downstream targets. (a) Visualization of CBD-associated gene expression changes along the NRF2 transcriptional network. Molecules shown in red were significantly upregulated by CBD (>2 × ). (b) Western blot analysis confirms ROS-dependent upregulation of NRF2 target proteins HMOX-1 and xCT, following 48 h treatment with CBD±40 μM VitE. (c) Subcellular fractionation using GSC 3832 cell line treated with CBD±VitE was used to generate protein lysates for western blot with the indicated antibodies. (d) Quantification of NRF2 levels using densitometry shows that relative to p84 (control), nuclear levels of NRF2 are enhanced by CBD treatment. (e) GSCs were transfected using the Qiagen Cignal Antioxidant Luciferase Reporter Kit (Qiagen Inc, Valencia, CA, USA; no. CCS-5020L) and Lipofectamine 2000 (Life Technologies) in OptiMEM media and 1% NEAA. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were treated with vehicle, 2.0 μM CBD, 2.0 μM CBD+40 μM VitE or dl-sulforapahane (40 μM) the manufacturer's recommended positive control for 48 h. NRF2 activity was measured using the Promega Dual-GLO Luciferase Assay system (Promega Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). First, NRF2-dependent luminescence was measured and then constitutively expressed luminescence was measured to normalize for cell number. The plotted luminescence units are a ratio of the two readings. Data were compared using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a corresponding Dunnett's post hoc test. *,#Statistically significant differences from control and CBD at P<0.05, respectively. (f) IHC detection of NRF2 and SLC7A11 (xCT) in GBM xenograft tissues from mice treated with vehicle or CBD for 22 days. Bar= 200 μm